Curcumin Inhibits Gastric Carcinoma Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 28077837
- PMCID: PMC5248567
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.902711
Curcumin Inhibits Gastric Carcinoma Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
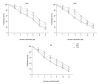
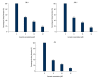
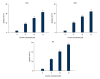
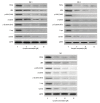
BACKGROUND Curcumin has well-known, explicit biological anti-tumor properties. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a central role in tumor cell proliferation and curcumin can regulate the Wnt/b-catenin signaling pathway of several carcinomas. The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of curcumin on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human gastric cancer cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS We used 3 gastric cancer cell lines: SNU-1, SNU-5, and AGS. Research methods used were MTT assay, flow cytometry, clonogenic assay, annexin V/PI method, Western blotting analysis, tumor formation assay, and in vivo in the TUNEL assay. RESULTS Curcumin markedly impaired tumor cell viability and induced apoptosis in vitro. Curcumin significantly suppressed the levels of Wnt3a, LRP6, phospho-LRP6, β-catenin, phospho-β-catenin, C-myc, and survivin. Xenograft growth in vivo was inhibited and the target genes of Wnt/β-catenin signaling were also reduced by curcumin treatment. CONCLUSIONS Curcumin exerts anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect in gastric cancer cells and in a xenograft model. Inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and the subsequently reduced expression of Wnt target genes show potential as a newly-identified molecular mechanism of curcumin treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
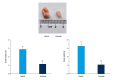
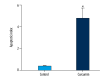

References
-
- Carmona-Bayonas A, Jimenez-Fonseca P, Lorenzo ML, et al. On the effect of triplet or doublet chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: Results from a National Cancer Registry. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14(11):1379–88. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Zhao PJ, Su D, et al. Paris saponin I induces apoptosis via increasing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 expression in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(6):2265–72. - PubMed
-
- Zhao P, Jiang H, Su D, et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation by mild hyperthermia at 43 C with Paris Saponin I in the lung adenocarcinoma cell line PC-9. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(1):327–32. - PubMed
-
- Zhao PJ, Song SC, Du LW, et al. Paris Saponins enhance radiosensitivity in a gefitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell line by inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle phase arrest. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2878–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

