Periosteal Distraction Osteogenesis: An Effective Method for Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 28078283
- PMCID: PMC5203878
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2075317
Periosteal Distraction Osteogenesis: An Effective Method for Bone Regeneration
Abstract
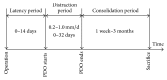
The treatment of bone defects is challenging and controversial. As a new technology, periosteal distraction osteogenesis (PDO) uses the osteogenicity of periosteum, which creates an artificial space between the bone surface and periosteum to generate new bone by gradually expanding the periosteum with no need for corticotomy. Using the newly formed bone of PDO to treat bone defects is effective, which can not only avoid the occurrence of immune-related complications, but also solve the problem of insufficient donor. This review elucidates the availability of PDO in the aspects of mechanisms, devices, strategies, and measures. Moreover, we also focus on the future prospects of PDO and hope that PDO will be applied to the clinical treatment of bone defects in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Patka P., Haarman H. J., Bakker F. C. Bone transplantation and bone replacement materials. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde. 1998;142(16):893–896. - PubMed
-
- Ilizarov G. A. The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues. Part I. The influence of stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 1989;(238):249–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

