Significance of oxygen transport through aquaporins
- PMID: 28079178
- PMCID: PMC5227684
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40411
Significance of oxygen transport through aquaporins
Abstract
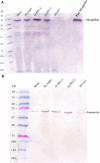
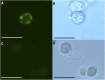
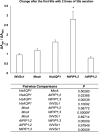
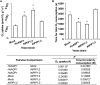
Aquaporins are membrane integral proteins responsible for the transmembrane transport of water and other small neutral molecules. Despite their well-acknowledged importance in water transport, their significance in gas transport processes remains unclear. Growing evidence points to the involvement of plant aquaporins in CO2 delivery for photosynthesis. The role of these channel proteins in the transport of O2 and other gases may also be more important than previously envisioned. In this study, we examined O2 permeability of various human, plant, and fungal aquaporins by co-expressing heterologous aquaporin and myoglobin in yeast. Two of the most promising O2-transporters (Homo sapiens AQP1 and Nicotiana tabacum PIP1;3) were confirmed to facilitate O2 transport in the spectrophotometric assay using yeast protoplasts. The over-expression of NtPIP1;3 in yeasts significantly increased their O2 uptake rates in suspension culture. In N. tabacum roots subjected to hypoxic hydroponic conditions, the transcript levels of the O2-transporting aquaporin NtPIP1;3 significantly increased after the seven-day hypoxia treatment, which was accompanied by the increase of ATP levels in the apical root segments. Our results suggest that the functional significance of aquaporin-mediated O2 transport and the possibility of controlling the rate of transmembrane O2 transport should be further explored.
Figures


References
-
- Benga G., Popescu O., Pop V. I. & Holmes R. p-(Chloromercuri)benzenesulfonate binding by membrane proteins and the inhibition of water transport in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry 25, 1535–1538 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Agre P. et al. Aquaporin CHIP: the archetypal molecular water channel. Am. J. Physiol. 265, F463–476 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Uehlein N., Lovisolo C., Siefritz F. & Kaldenhoff R. The tobacco aquaporin NtAQP1 is a membrane CO2 pore with physiological functions. Nature 425, 734–737 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Navarro-Ródenas A., Ruíz-Lozano J. M., Kaldenhoff R. & Morte A. The aquaporin TcAQP1 of the desert truffle Terfezia claveryi is a membrane pore for water and CO2 transport. Mol. Plant Microbe. In. 25, 259–266 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Uehlein N., Sperling H., Heckwolf M. & Kaldenhoff R. The Arabidopsis aquaporin PIP1; 2 rules cellular CO2 uptake. Plant Cell Environ. 35, 1077–1083 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

