Brief online interventions targeting risk and protective factors for increased and problematic alcohol use among American college students studying abroad
- PMID: 28080092
- PMCID: PMC5344728
- DOI: 10.1037/adb0000242
Brief online interventions targeting risk and protective factors for increased and problematic alcohol use among American college students studying abroad
Abstract
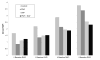
Research documents increased and problematic alcohol use during study abroad experiences for college students yet no research documents effective preventive programs with these students. The present randomized controlled trial was designed to prevent increased and problematic alcohol use abroad by correcting misperceptions of peer drinking norms abroad and by promoting positive and healthy adjustment into the host culture (i.e., sojourner adjustment) through brief online personalized feedback interventions. A sample of 343 study abroad college students was randomly assigned to 1 of 4 conditions including a personalized normative feedback intervention (PNF), a sojourner adjustment feedback intervention (SAF), a combined PNF + SAF intervention, and an assessment-only control condition. Generalized estimated equation analyses accounting for baseline drinking and consequences revealed an intervention effect for PNF that was mitigated by baseline drinking level, such that PNF was best for those with lighter baseline drinking, but heavier baseline drinkers receiving PNF alone or PNF + SAF drank comparatively similar or more heavily abroad to those in the control condition. However, PNF + SAF condition participants with greater baseline levels of consequences reported comparatively less consequences abroad than their control participants. Thus, PNF alone may be helpful for lighter drinkers at predeparture and the addition of SAF to PNF may help prevent consequences abroad for those reporting more consequences prior to departure abroad. This research represents an important first step in designing and implementing efficacious interventions with at-risk study abroad college students, for which no current empirically based programs exist. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2017 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures

References
-
- Association of Americans Resident Overseas. [Accessed September 16, 2015];6.32 million Americans (excluding military) live in 160-plus countries. 2013 from http://aaro.org/about-aaro/6m-americans-abroad.
-
- Babor TF, Higgins JC. Alcohol screening and brief interventions: Dissemination strategies for medical practice and public health. Addiction. 2000;95:677–686. - PubMed
-
- Babor TF, Stephens RS, Marlatt GA. Verbal reports methods in clinical research on alcoholism: Report bias and its minimization. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1987;48:410–424. - PubMed
-
- Baer JS. Student factors: Understanding individual variation in college drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 2002;(Suppl 14):40–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

