Chemical probes targeting epigenetic proteins: Applications beyond oncology
- PMID: 28080202
- PMCID: PMC5453191
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2017.1279371
Chemical probes targeting epigenetic proteins: Applications beyond oncology
Abstract
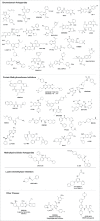
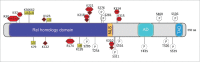
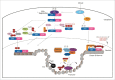
Epigenetic chemical probes are potent, cell-active, small molecule inhibitors or antagonists of specific domains in a protein; they have been indispensable for studying bromodomains and protein methyltransferases. The Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC), comprising scientists from academic and pharmaceutical laboratories, has generated most of the current epigenetic chemical probes. Moreover, the SGC has shared about 4 thousand aliquots of these probes, which have been used primarily for phenotypic profiling or to validate targets in cell lines or primary patient samples cultured in vitro. Epigenetic chemical probes have been critical tools in oncology research and have uncovered mechanistic insights into well-established targets, as well as identify new therapeutic starting points. Indeed, the literature primarily links epigenetic proteins to oncology, but applications in inflammation, viral, metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases are now being reported. We summarize the literature of these emerging applications and provide examples where existing probes might be used.
Keywords: Bromodomain; cardiovascular disease; histone arginine methyltransferase; histone lysine demethylase; histone lysine methyltransferase; inflammation; viral disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Open access chemical probes for epigenetic targets.Future Med Chem. 2015;7(14):1901-17. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.127. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26397018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The bromodomain: from epigenome reader to druggable target.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1839(8):676-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.03.011. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24686119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic small molecule modulators of histone and DNA methylation.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Aug;45:73-85. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29579619 Review.
-
Histone H4 acetylation differentially modulates arginine methylation by an in Cis mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 10;286(23):20323-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.207258. Epub 2011 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21502321 Free PMC article.
-
Histone methylation versus histone acetylation: new insights into epigenetic regulation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;13(3):263-73. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00208-8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11343896 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics of Skeletal Diseases.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018 Jun;16(3):246-255. doi: 10.1007/s11914-018-0435-y. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018. PMID: 29574535 Review.
-
The histone methyltransferase inhibitor A-366 enhances hemoglobin expression in erythroleukemia cells upon co-exposure with chemical inducers in culture.J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2021 Jan 6;28(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40709-020-00132-3. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2021. PMID: 33407944 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic drugs: More than meets the eye.Epigenetics. 2017 May 4;12(5):307. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2017.1322881. Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 28541128 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dysregulation of lysine acetylation in the pathogenesis of digestive tract cancers and its clinical applications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Sep 26;12:1447939. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1447939. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39391349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRMT inhibitor promotes SMN2 exon 7 inclusion and synergizes with nusinersen to rescue SMA mice.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Nov 8;15(11):e17683. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202317683. Epub 2023 Sep 19. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37724723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrowsmith CH, Audia JE, Austin C, Baell J, Bennett J, Blagg J, Bountra C, Brennan PE, Brown PJ, Bunnage ME, et al.. The promise and peril of chemical probes. Nat Chem Biol 2015; 11:536-41; PMID:26196764; https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1867 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown PJ, Muller S. Open access chemical probes for epigenetic targets. Future Med Chem 2015; 7:1901-17; PMID:26397018; https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.127 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bunnage ME. Getting pharmaceutical R&D back on target. Nat Chem Biol 2011; 7:335-9; PMID:21587251; https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.581 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frye SV. The art of the chemical probe. Nat Chem Biol 2010; 6:159-61; PMID:20154659; https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.296 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muller S, Brown PJ. Epigenetic chemical probes. Clin Pharmacol Therap 2012; 92:689-93; PMID:23093316; https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2012.154 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
