Clinical implications of globally emerging azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 28080986
- PMCID: PMC5095539
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0460
Clinical implications of globally emerging azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
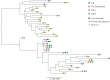
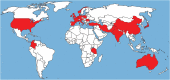
Aspergillus fungi are the cause of an array of diseases affecting humans, animals and plants. The triazole antifungal agents itraconazole, voriconazole, isavuconazole and posaconazole are treatment options against diseases caused by Aspergillus However, resistance to azoles has recently emerged as a new therapeutic challenge in six continents. Although de novo azole resistance occurs occasionally in patients during azole therapy, the main burden is the aquisition of resistance through the environment. In this setting, the evolution of resistance is attributed to the widespread use of azole-based fungicides. Although ubiquitously distributed, A. fumigatus is not a phytopathogen. However, agricultural fungicides deployed against plant pathogenic moulds such as Fusarium, Mycospaerella and A. flavus also show activity against A. fumigatus in the environment and exposure of non-target fungi is inevitable. Further, similarity in molecule structure between azole fungicides and antifungal drugs results in cross-resistance of A. fumigatus to medical azoles. Clinical studies have shown that two-thirds of patients with azole-resistant infections had no previous history of azole therapy and high mortality rates between 50% and 100% are reported in azole-resistant invasive aspergillosis. The resistance phenotype is associated with key mutations in the cyp51A gene, including TR34/L98H, TR53 and TR46/Y121F/T289A resistance mechanisms. Early detection of resistance is of paramount importance and if demonstrated, either with susceptibility testing or through molecular analysis, azole monotherapy should be avoided. Liposomal amphotericin B or a combination of voriconazole and an echinocandin are recomended for azole-resistant aspergillosis.This article is part of the themed issue 'Tackling emerging fungal threats to animal health, food security and ecosystem resilience'.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; azole resistance; epidemiology; fungicides; treatment; worldwide emergence.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
