Host-to-Host Transmission of Streptococcus pneumoniae Is Driven by Its Inflammatory Toxin, Pneumolysin
- PMID: 28081446
- PMCID: PMC5267320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.12.005
Host-to-Host Transmission of Streptococcus pneumoniae Is Driven by Its Inflammatory Toxin, Pneumolysin
Abstract
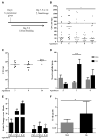
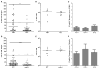
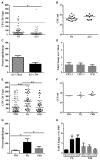
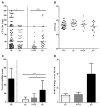
Host-to-host transmission is a critical step for infection. Here we studied transmission of the opportunistic pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae in an infant mouse model. Transmission from nasally colonized pups required high levels of bacterial shedding in nasal secretions and was temporally correlated with, and dependent upon, the acute inflammatory response. Pneumolysin, a pore-forming cytotoxin and major virulence determinant, was both necessary and sufficient to promote inflammation, which increased shedding and allowed for intralitter transmission. Direct contact between pups was not required for transmission indicating the importance of an environmental reservoir. An additional in vivo effect of pneumolysin was to enhance bacterial survival outside of the host. Our findings provide experimental evidence of a microbial strategy for transit to new hosts and explain why an organism expresses a toxin that damages the host upon which it depends.
Keywords: bacteria; colonization; infection; pneumococcus; pneumolysin; shedding; toxin; transmission.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
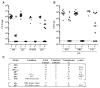
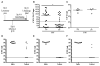
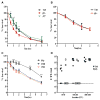
Comment in
-
Host-to-Host Transmission of the Pneumococcus-New Victims of a Toxic Relationship.Cell Host Microbe. 2017 Jan 11;21(1):5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.12.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2017. PMID: 28081444
References
-
- Albiger B, Dahlberg S, Sandgren A, Wartha F, Beiter K, Katsuragi H, Akira S, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B. Toll-like receptor 9 acts at an early stage in host defence against pneumococcal infection. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:633–644. - PubMed
-
- Bachman M, Weiser J. The competition for metals among microbes and their host. In: Nriagu J, Skaar E, editors. Trace Metals and Infectious Disease. MIT Press; 2015. pp. 29–38. - PubMed
-
- Bernatoniene J, Zhang Q, Dogan S, Mitchell TJ, Paton JC, Finn A. Induction of CC and CXC chemokines in human antigen-presenting dendritic cells by the pneumococcal proteins pneumolysin and CbpA, and the role played by toll-like receptor 4, NF-kappaB, and mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Infect Dis. 2008;198:1823–1833. - PubMed
-
- Chen A, Mann B, Gao G, Heath R, King J, Maissoneuve J, Alderson M, Tate A, Hollingshead SK, Tweten RK, et al. Multivalent pneumococcal protein vaccines comprising pneumolysoid with epitopes/fragments of CbpA and/or PspA elicit strong and broad protection. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015;22:1079–1089. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

