Kidney dysfunction, systemic inflammation and mental well-being in elderly post-myocardial infarction patients
- PMID: 28081723
- PMCID: PMC5228176
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-016-0170-z
Kidney dysfunction, systemic inflammation and mental well-being in elderly post-myocardial infarction patients
Abstract
Background: The aim was to investigate whether mild kidney dysfunction and low-grade inflammation in post-myocardial infarction patients are independently associated with markers of mental well-being (i.e. depressive and apathy symptoms, and dispositional optimism).
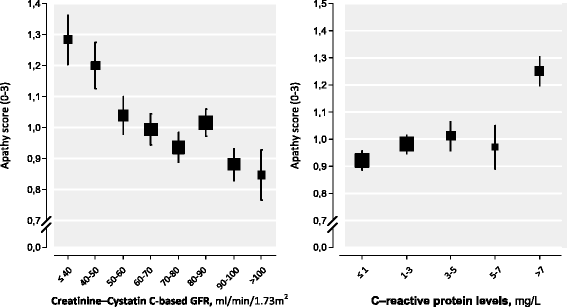
Methods: In post-myocardial infarction patients, kidney function was assessed by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) calculated from the combined CKD-EPI formula based on serum levels of both creatinine and cystatine C. Systemic inflammation was assessed using high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels. The 15-item Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-15), the 3-item apathy subscale and the 4-item optimism questionnaire (4Q) were used to measure mental well-being and were analyzed using linear multivariable regression analysis.
Results: Of the 2355 patients, mean age was 72.3 (range 63-84) years and 80.1% were men. After multivariable adjustment, a poorer kidney function was associated with more depressive symptoms (β = -0.084, p < 0.001), more apathy symptoms (β = -0.101, p < 0.001), and less dispositional optimism (β = 0.072, p = 0.002). Moreover, higher levels of hs-CRP were associated with more depressive symptoms (β = 0.051, p = 0.013), more apathy symptoms (β = 0.083, p < 0.001) and less dispositional optimism (β = -0.047 p = 0.024). Apathy showed the strongest independent relation with both low eGFR and high hs-CRP.
Conclusions: In post-myocardial infarction patients, impaired kidney function and systemic inflammation showed a stronger association with apathy than with depressive symptoms and dispositional optimism.
Keywords: Apathy; Depressive symptoms; Dispositional optimism; Kidney dysfunction; Myocardial infarction; Systemic inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical activity after myocardial infarction: is it related to mental health?Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2013 Jun;20(3):399-408. doi: 10.1177/2047487312438184. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22345693 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary patterns and mental health after myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 16;12(10):e0186368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186368. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29036212 Free PMC article.
-
Association of n-3 long-chain PUFA and fish intake with depressive symptoms and low dispositional optimism in older subjects with a history of myocardial infarction.Br J Nutr. 2010 May;103(9):1381-7. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509993308. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 19968890
-
Apathy and depressive symptoms in older people and incident myocardial infarction, stroke, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data.Clin Epidemiol. 2018 Apr 4;10:363-379. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S150915. eCollection 2018. Clin Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29670402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the dispositional optimism and depression in young people: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Psicol Reflex Crit. 2021 Nov 29;34(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s41155-021-00202-y. Psicol Reflex Crit. 2021. PMID: 34842988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of genetic variation of human metabolism for BMI, mental traits and mental disorders.Mol Metab. 2018 Jun;12:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.03.015. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Mol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29673576 Free PMC article.
-
Family meals are associated with lower substance use in female adolescents.Fam Process. 2025 Mar;64(1):e13039. doi: 10.1111/famp.13039. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Fam Process. 2025. PMID: 39082079 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Lipophilic Beta-Blockers and Depression in Diabetic Patients on Chronic Dialysis.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022 Aug 29;15:11795514221119446. doi: 10.1177/11795514221119446. eCollection 2022. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 36061232 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and Acceptability of a Peer Influencer Delivered Social Media Based Intervention to Promote Mental Health Awareness for Young Black and Latinx Gay and Bisexual Men and Transgender Women.J Gay Lesbian Ment Health. 2025;29(1):28-44. doi: 10.1080/19359705.2023.2239730. Epub 2023 Aug 3. J Gay Lesbian Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40114682
-
Insights into youth nutritional status in Serbia: assessing prevalence and trend in the context of social determinants.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 22;25(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21474-4. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39844149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lichtman JH, Froelicher ES, Blumenthal JA, Carney RM, Doering LV, Frasure-Smith N, et al. Depression as a risk factor for poor prognosis among patients with acute coronary syndrome: Systematic review and recommendations a scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2014;129:1350–69. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000019. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

