Vps33b is crucial for structural and functional hepatocyte polarity
- PMID: 28082148
- PMCID: PMC5387182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.01.001
Vps33b is crucial for structural and functional hepatocyte polarity
Abstract
Background & aims: In the normal liver, hepatocytes form a uniquely polarised cell layer that enables movement of solutes from sinusoidal blood to canalicular bile. Whilst several cholestatic liver diseases with defects of hepatocyte polarity have been identified, the molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis are not well defined. One example is arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis syndrome, which in most patients is caused by VPS33B mutations. VPS33B is a protein involved in membrane trafficking that interacts with RAB11A at recycling endosomes. To understand the pathways that regulate hepatocyte polarity better, we investigated VPS33B deficiency using a novel mouse model with a liver-specific Vps33b deletion.
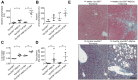
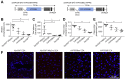
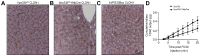
Methods: To assess functional polarity, plasma and bile samples were collected from Vps33b liver knockout (Vps33bfl/fl-AlfpCre) and control (Vps33bfl/fl) mice; bile components or injected substrates were quantitated by mass spectrometry or fluorometry. For structural analysis, livers underwent light and transmission electron microscopy. Apical membrane and tight junction protein localisation was assessed by immunostaining. Adeno-associated virus vectors were used for in vivo gene rescue experiments.
Results: Like patients, Vps33bfl/fl-AlfpCre mice showed mislocalisation of ATP-binding cassette proteins that are specifically trafficked to the apical membrane via Rab11a-positive recycling endosomes. This was associated with retention of bile components in blood. Loss of functional tight junction integrity and depletion of apical microvilli were seen in knockout animals. Gene transfer partially rescued these defects.
Conclusions: Vps33b has a key role in establishing structural and functional aspects of hepatocyte polarity and may be a target for gene replacement therapy.
Lay summary: Hepatocytes are liver cells with tops and bottoms; that is, they are polarised. At their bottoms they absorb substances from blood. They then, at their tops, secrete these substances and their metabolites into bile. When polarity is lost, this directional flow of substances from blood to bile is disrupted and liver disease follows. In this study, using a new mouse model with a liver-specific mutation of Vps33b, the mouse version of a gene that is mutated in most patients with arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis (ARC) syndrome, we investigated how the Vps33b gene product contributes to establishing hepatocyte polarity. We identified in these mice abnormalities similar to those in children with ARC syndrome. Gene transfer could partly reverse the mouse abnormalities. Our work contributes to the understanding of VPS33B disease and hepatocyte polarity in general, and may point towards gene transfer mediated treatment of ARC liver disease.
Keywords: Bile; Bile canaliculi; Canalicular membrane; Cholestasis; Gene transfer; Hepatocyte polarity; Liver diseases; Protein trafficking; Rab11a; Vps33b.
Copyright © 2017 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Cereijido M., Contreras R.G., Shoshani L. Cell adhesion, polarity, and epithelia in the dawn of metazoans. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:1229–1262. - PubMed
-
- Carlton V.E.H., Harris B.Z., Puffenberger E.G., Batta A.K., Knisely A.S., Robinson D.L. Complex inheritance of familial hypercholanemia with associated mutations in TJP2 and BAAT. Nat Genet. 2003;34:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Girard M., Lacaille F., Verkarre V., Mategot R., Feldmann G., Grodet A. MYO5B and bile salt export pump contribute to cholestatic liver disorder in microvillous inclusion disease. Hepatology. 2014;60:301–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

