Regulating effect of TongXie-YaoFang on colonic epithelial secretion via Cl- and HCO3- channel
- PMID: 28082810
- PMCID: PMC5192269
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i48.10584
Regulating effect of TongXie-YaoFang on colonic epithelial secretion via Cl- and HCO3- channel
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the pharmacological effect of TongXie-YaoFang (TXYF) formula, a Chinese herbal formula, on Diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (D-IBS) rats.
Methods: In a neonatal maternal separation plus restraint stress (NMS + RS) model of D-IBS, male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into two groups (NMS + RS group and TXYF-formula group) with no handlings were used as controls (NH group). Starting from postnatal day 60, rats in TXYF-formula group were administered TXYF-formula (4.92 g/100 g bodyweight) orally twice a day for 14 consecutive days while NH group and NMS + RS group were given distilled water. Using short-circuit current technology, we observed 5-HT-induced changes of current across ion channels, such as cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) Cl- channel, epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC), Ca2+-dependent Cl- channel (CACC), Na+-K+-2Cl- co-transporter (NKCC), and Na+-HCO3- co-transporter (NBC), in the colonic epithelium of three groups after exposure to drugs and specific blockers with a Power Lab System (AD Instruments International).
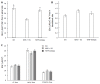
Results: Under basal conditions, the changes of short-circuit current (∆Isc, µA/cm2) induced by 5-HT were similar in NH group and TXYF-formula group, and both higher than NMS + RS group (70.86 µA/cm2 ± 12.32 µA/cm2, 67.67 µA/cm2 ± 11.68 µA/cm2vs 38.8 µA/cm2 ± 7.25 µA/cm2, P < 0.01, respectively). When CACC was blocked by 4,4'-diisothiocyanato-stilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid, 5-HT-induced ∆Isc was smaller in NMS + RS group than in NH group and TXYF-formula group, respectively (48.41 µA/cm2 ± 13.15 µA/cm2vs 74.62 µA/cm2 ± 10.73 µA/cm2, 69.22 µA/cm2 ± 11.7 µA/cm2, P < 0.05, respectively). The similar result could be obtained when ENaC was blocked by Amiloride (44.69 µA/cm2 ± 12.58 µA/cm2vs 62.05 µA/cm2 ± 11.26 µA/cm2, 62.11 µA/cm2 ± 12.01 µA/cm2, P < 0.05, respectively). However, when CFTR Cl- channel was blocked by 1,1-dimethyl piperidinium chloride (DPC), 5-HT-induced ∆Isc did not significantly differ in three groups (42.28 µA/cm2 ± 10.61 µA/cm2vs 51.48 µA/cm2 ± 6.56 µA/cm2vs 47.75 µA/cm2 ± 7.99 µA/cm2, P > 0.05, respectively). The similar results could also be obtained in three groups when NBC and NKCC were respectively blocked by their blockers.
Conclusion: TXYF-formula can regulate the Cl- and HCO3- secretion of colonic mucosa via CFTR Cl- channel, Cl-/HCO3- exchanger, NBC and NKCC co-transporters.
Keywords: Colonic mucosa; Diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome; Ion channel; Short-circuit current; TongXie-YaoFang formula.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of TongXie-YaoFang formula on colonic contraction in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar 14;21(10):2912-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2912. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25780288 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of TongXie-YaoFang on Cl(-) and HCO3 (-) Transport in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7954982. doi: 10.1155/2016/7954982. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27403199 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of shugan jianpi recipe on the ion transport of diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome rat colon mucosa induced by 5-HT].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Nov;32(11):1516-20. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23359977 Chinese.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of Chinese herbal formula Tongxie Yaofang for diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence for clinical practice and future trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 25;13:904657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.904657. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091782 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cl- Electrolyte Permeability in Epithelia by Active Traditional Chinese Medicine Monomers for Diarrhea.Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(9):902-909. doi: 10.2174/1389450121666200504073635. Curr Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32364074 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulation roles of miRNAs in Helicobacter pylori infection.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jul;25(7):1929-1939. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03094-9. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36781601 Review.
-
Mucosa repair mechanisms of Tong-Xie-Yao-Fang mediated by CRH-R2 in murine, dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Apr 28;24(16):1766-1778. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1766. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29713130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ford AC, Bercik P, Morgan DG, Bolino C, Pintos-Sanchez MI, Moayyedi P. Validation of the Rome III criteria for the diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome in secondary care. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1262–70.e1. - PubMed
-
- Shalaby SA, Sayed MM, Ibrahim WA, Abdelhakam SM, Rushdy M. The prevalence of coeliac disease in patients fulfilling Rome III criteria for irritable bowel syndrome. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2016;17:73–77. - PubMed
-
- Nee J, Zakari M, Lembo AJ. Current and emerging drug options in the treatment of diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16:2781–2792. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

