DOPAL derived alpha-synuclein oligomers impair synaptic vesicles physiological function
- PMID: 28084443
- PMCID: PMC5233976
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40699
DOPAL derived alpha-synuclein oligomers impair synaptic vesicles physiological function
Abstract
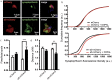
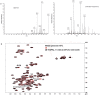
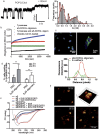
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons and by accumulation of alpha-synuclein (aS) aggregates in the surviving neurons. The dopamine catabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) is a highly reactive and toxic molecule that leads to aS oligomerization by covalent modifications to lysine residues. Here we show that DOPAL-induced aS oligomer formation in neurons is associated with damage of synaptic vesicles, and with alterations in the synaptic vesicles pools. To investigate the molecular mechanism that leads to synaptic impairment, we first aimed to characterize the biochemical and biophysical properties of the aS-DOPAL oligomers; heterogeneous ensembles of macromolecules able to permeabilise cholesterol-containing lipid membranes. aS-DOPAL oligomers can induce dopamine leak in an in vitro model of synaptic vesicles and in cellular models. The dopamine released, after conversion to DOPAL in the cytoplasm, could trigger a noxious cycle that further fuels the formation of aS-DOPAL oligomers, inducing neurodegeneration.
Figures



References
-
- German D. C., Manaye K., Smith W. K., Woodward D. J. & Saper C. B. Midbrain dopaminergic cell loss in Parkinson’s disease: computer visualization. Ann Neurol 26, 507–514 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Bisaglia M., Greggio E., Beltramini M. & Bubacco L. Dysfunction of dopamine homeostasis: Clues in the hunt for novel Parkinson’s disease therapies. FASEB J 27, 2101–2110 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Galvin J. E. Interaction of alpha-synuclein and dopamine metabolites in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: a case for the selective vulnerability of the substantia nigra. Acta Neuropathol 112, 115–126 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

