A Pilot Study Linking Endothelial Injury in Lungs and Kidneys in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 28085500
- PMCID: PMC5470750
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201609-1765OC
A Pilot Study Linking Endothelial Injury in Lungs and Kidneys in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
Rationale: Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) frequently have albuminuria (indicative of renal endothelial cell injury) associated with hypoxemia.
Objectives: To determine whether (1) cigarette smoke (CS)-induced pulmonary and renal endothelial cell injury explains the association between albuminuria and COPD, (2) CS-induced albuminuria is linked to increases in the oxidative stress-advanced glycation end products (AGEs) receptor for AGEs (RAGE) pathway, and (3) enalapril (which has antioxidant properties) limits the progression of pulmonary and renal injury by reducing activation of the AGEs-RAGE pathway in endothelial cells in both organs.
Methods: In 26 patients with COPD, 24 ever-smokers without COPD, 32 nonsmokers who underwent a renal biopsy or nephrectomy, and in CS-exposed mice, we assessed pathologic and ultrastructural renal lesions, and measured urinary albumin/creatinine ratios, tissue oxidative stress levels, and AGEs and RAGE levels in pulmonary and renal endothelial cells. The efficacy of enalapril on pulmonary and renal lesions was assessed in CS-exposed mice.
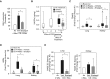
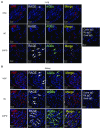
Measurements and main results: Patients with COPD and/or CS-exposed mice had chronic renal injury, increased urinary albumin/creatinine ratios, and increased tissue oxidative stress and AGEs-RAGE levels in pulmonary and renal endothelial cells. Treating mice with enalapril attenuated CS-induced increases in urinary albumin/creatinine ratios, tissue oxidative stress levels, endothelial cell AGEs and RAGE levels, pulmonary and renal cell apoptosis, and the progression of chronic renal and pulmonary lesions.
Conclusions: Patients with COPD and/or CS-exposed mice have pulmonary and renal endothelial cell injury linked to increased endothelial cell AGEs and RAGE levels. Albuminuria could identify patients with COPD in whom angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy improves renal and lung function by reducing endothelial injury.
Keywords: COPD; cigarette smoke; comorbidities; endothelium; kidney.
Figures
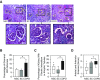
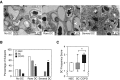
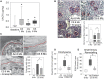
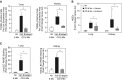
Comment in
-
EnRAGEed Kidneys in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Jun 1;195(11):1411-1413. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0173ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28569576 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Voelkel: Cigarette Smoke Is an Endothelial Cell Toxin.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan 15;197(2):274-275. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201707-1381LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 28726486 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cigarette Smoke Is an Endothelial Cell Toxin.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Jan 15;197(2):274. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201706-1123LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 28726501 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mannino DM, Buist AS. Global burden of COPD: risk factors, prevalence, and future trends. Lancet. 2007;370:765–773. - PubMed
-
- Divo M, Cote C, de Torres JP, Casanova C, Marin JM, Pinto-Plata V, Zulueta J, Cabrera C, Zagaceta J, Hunninghake G, et al. BODE Collaborative Group. Comorbidities and risk of mortality in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:155–161. - PubMed
-
- Pedrinelli R, Dell’Omo G, Di Bello V, Pellegrini G, Pucci L, Del Prato S, Penno G. Low-grade inflammation and microalbuminuria in hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:2414–2419. - PubMed
-
- Warram JH, Gearin G, Laffel L, Krolewski AS. Effect of duration of type I diabetes on the prevalence of stages of diabetic nephropathy defined by urinary albumin/creatinine ratio. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:930–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

