Self-regulating ubiquitin ligases
- PMID: 28087580
- PMCID: PMC5694948
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201696154
Self-regulating ubiquitin ligases
Abstract
Occasional auto‐modification of ubiquitin ligases typically leads to their proteasomal destruction, but new findings published in The
Figures
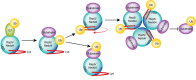
Comment on
-
Ubiquitylation-dependent oligomerization regulates activity of Nedd4 ligases.EMBO J. 2017 Feb 15;36(4):425-440. doi: 10.15252/embj.201694314. Epub 2017 Jan 9. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28069708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CAP (2009) RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem 78: 1 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

