Thirty Years of Evidence on the Efficacy of Drug Treatments for Chronic Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 28087688
- PMCID: PMC5265698
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003529
Thirty Years of Evidence on the Efficacy of Drug Treatments for Chronic Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Treatments that reduce mortality and morbidity in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB), β-blockers (BB), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), have not been studied in a head-to-head fashion. This network meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy of these drugs and their combinations regarding all-cause mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
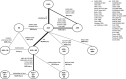
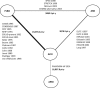
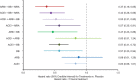
Methods and results: A systematic literature review identified 57 randomized controlled trials published between 1987 and 2015, which were compared in terms of study and patient characteristics, baseline risk, outcome definitions, and the observed treatment effects. Despite differences identified in terms of study duration, New York Heart Association class, ejection fraction, and use of background digoxin, a network meta-analysis was considered feasible and all trials were analyzed simultaneously. The random-effects network meta-analysis suggested that the combination of ACEI+BB+MRA was associated with a 56% reduction in mortality versus placebo (hazard ratio 0.44, 95% credible interval 0.26-0.66); ARNI+BB+MRA was associated with the greatest reduction in all-cause mortality versus placebo (hazard ratio 0.37, 95% credible interval 0.19-0.65). A sensitivity analysis that did not account for background therapy suggested that ARNI monotherapy is more efficacious than ACEI or ARB monotherapy.
Conclusions: The network meta-analysis showed that treatment with ACEI, ARB, BB, MRA, and ARNI and their combinations were better than the treatment with placebo in reducing all-cause mortality, with the exception of ARB monotherapy and ARB plus ACEI. The combination of ARNI+BB+MRA resulted in the greatest mortality reduction.
Keywords: drug combinations; drug therapy; heart failure; mortality; network meta-analysis.
© 2017 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Køber L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Rønnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A, Bax JJ, Baumgartner H, Ceconi C, Dean V, Deaton C, Fagard R, Funck-Brentano C, Hasdai D, Hoes A, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, McDonagh T, Moulin C, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Vahanian A, Windecker S, McDonagh T, Sechtem U, Bonet LA, Avraamides P, Ben Lamin HA, Brignole M, Coca A, Cowburn P, Dargie H, Elliott P, Flachskampf FA, Guida GF, Hardman S, Iung B, Merkely B, Mueller C, Nanas JN, Nielsen OW, Orn S, Parissis JT, Ponikowski P Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14:803–869. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfs105. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, Gillespie C, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho PM, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott MM, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino M, Nichol G, Roger VL, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:948–954. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192666. - PubMed
-
- Loehr LR, Rosamond WD, Chang PP, Folsom AR, Chambless LE. Heart failure incidence and survival (from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study). Am J Cardiol. 2008;101:1016–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.061. - PubMed
-
- Zannad F, Agrinier N, Alla F. Heart failure burden and therapy. Europace. 2009;11(suppl 5):v1–v9. doi: 10.1093/europace/eup304. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, González-Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GM, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P Authors/Task Force Members. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2129–2200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

