Amygdala and hippocampus are symptomatogenic zones for central apneic seizures
- PMID: 28087822
- PMCID: PMC5317387
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003613
Amygdala and hippocampus are symptomatogenic zones for central apneic seizures
Abstract
Objective: To identify limbic sites of respiratory control in the human brain, and by extension, the symptomatogenic zone for central apnea.
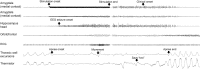
Methods: We used direct stimulation of anatomically, precisely placed stereotactic EEG electrodes to analyze breathing responses. We prospectively studied 3 patients who were explored with stereotactically implanted depth electrodes. The amygdala and hippocampus, as well as extralimbic sites (orbitofrontal, temporal tip, and temporal neocortex), were investigated.
Results: Individual stimulation of the amygdala and hippocampal head consistently elicited central apnea in the expiratory phase, as did exquisitely focal hippocampal seizures.
Conclusions: These findings confirm that hippocampus and amygdala are limbic breathing control sites in humans, as well as the symptomatogenic zone for central apneic seizures.
© 2017 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Ryvlin P, Nashef L, Lhatoo SD, et al. Incidence and mechanisms of cardiorespiratory arrests in epilepsy monitoring units (MORTEMUS): a retrospective study. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:966–977. - PubMed
-
- Nadkarni MA, Friedman D, Devinsky O. Central apnea at complex partial seizure onset. Seizure 2012;21:555–558. - PubMed
-
- Schuele SU, Afshari M, Afshari ZS, et al. Ictal central apnea as a predictor for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 2011;22:401–403. - PubMed
-
- Tezer FI, Remi J, Noachtar S. Ictal apnea of epileptic origin. Neurology 2009;72:855–857. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
