Role of STIM2 in cell function and physiopathology
- PMID: 28087881
- PMCID: PMC5430229
- DOI: 10.1113/JP273889
Role of STIM2 in cell function and physiopathology
Abstract
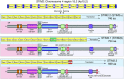
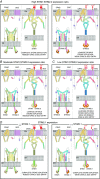
An endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident protein that regulates cytosolic and ER free-Ca2+ concentration by induction of store-operated calcium entry: that is the original definition of STIM2 and its function. While its activity strongly depends on the amount of calcium stored in the ER, its function goes further, to intracellular signalling and gene expression. Initially under-studied owing to the prominent function of STIM1, STIM2 came to be regarded as vital in mice, gradually emerging as an important player in the nervous system, and cooperating with STIM1 in the immune system. STIM2 has also been proposed as a relevant player in pathological conditions related to ageing, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, autoimmune disorders and cancer. The discovery of additional functions, together with new splicing forms with opposite roles, has clarified existing controversies about STIM2 function in SOCE. With STIM2 being essential for life, but apparently not for development, newly available data demonstrate a complex and still intriguing behaviour that this review summarizes, updating current knowledge of STIM2 function.
Keywords: STIM2; calcium entry; store-operated calcium entry.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Aytes A, Mollevi DG, Martinez‐Iniesta M, Nadal M, Vidal A, Morales A, Salazar R, Capella G & Villanueva A (2012). Stromal interaction molecule 2 (STIM2) is frequently overexpressed in colorectal tumors and confers a tumor cell growth suppressor phenotype. Mol Carcinog 51, 746–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

