Pharmacological rescue of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a mouse model of X-linked intellectual disability
- PMID: 28088401
- PMCID: PMC5346071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.01.003
Pharmacological rescue of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a mouse model of X-linked intellectual disability
Abstract
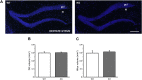
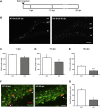
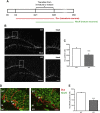
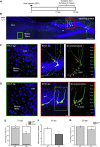
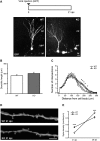
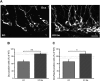
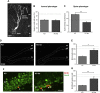
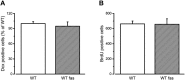
Oligophrenin-1 (OPHN1) is a Rho GTPase activating protein whose mutations cause X-linked intellectual disability (XLID). How loss of function of Ophn1 affects neuronal development is only partly understood. Here we have exploited adult hippocampal neurogenesis to dissect the steps of neuronal differentiation that are affected by Ophn1 deletion. We found that mice lacking Ophn1 display a reduction in the number of newborn neurons in the dentate gyrus. A significant fraction of the Ophn1-deficient newly generated neurons failed to extend an axon towards CA3, and showed an altered density of dendritic protrusions. Since Ophn1-deficient mice display overactivation of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) and protein kinase A (PKA) signaling, we administered a clinically approved ROCK/PKA inhibitor (fasudil) to correct the neurogenesis defects. While administration of fasudil was not effective in rescuing axon formation, the same treatment completely restored spine density to control levels, and enhanced the long-term survival of adult-born neurons in mice lacking Ophn1. These results identify specific neurodevelopmental steps that are impacted by Ophn1 deletion, and indicate that they may be at least partially corrected by pharmacological treatment.
Keywords: Axon extension; Dendritic spines; Fasudil; Rho GTPase.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROCK/PKA Inhibition Rescues Hippocampal Hyperexcitability and GABAergic Neuron Alterations in a Oligophrenin-1 Knock-Out Mouse Model of X-Linked Intellectual Disability.J Neurosci. 2020 Mar 25;40(13):2776-2788. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0462-19.2020. Epub 2020 Feb 25. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32098904 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase A Deregulation in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Impairs Working Memory in Murine Oligophrenin-1 Deficiency.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 15;37(46):11114-11126. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0351-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 13. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29030432 Free PMC article.
-
Rho Kinase Inhibition Is Essential During In Vitro Neurogenesis and Promotes Phenotypic Rescue of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons With Oligophrenin-1 Loss of Function.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):860-9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0303. Epub 2016 May 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27160703 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the phenotypic spectrum associated with OPHN1 mutations: Report of 17 individuals with intellectual disability but no cerebellar hypoplasia.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Aug;61(8):442-450. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29510240 Review.
-
Rho GTPase signaling at the synapse: implications for intellectual disability.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Sep 10;319(15):2368-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.05.033. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23769912 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity Are Differentially Altered during Postnatal Development by Loss of the X-Linked Intellectual Disability Protein Oligophrenin-1.Cells. 2022 May 5;11(9):1545. doi: 10.3390/cells11091545. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563851 Free PMC article.
-
Repulsive Guidance Molecule A Suppresses Adult Neurogenesis.Stem Cell Reports. 2020 Apr 14;14(4):677-691. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Stem Cell Reports. 2020. PMID: 32243839 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases in Intellectual Disability: From Genetics to Therapeutic Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 20;19(6):1821. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061821. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29925821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROCK/PKA Inhibition Rescues Hippocampal Hyperexcitability and GABAergic Neuron Alterations in a Oligophrenin-1 Knock-Out Mouse Model of X-Linked Intellectual Disability.J Neurosci. 2020 Mar 25;40(13):2776-2788. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0462-19.2020. Epub 2020 Feb 25. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32098904 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis in intellectual disabilities.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45044-45045. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18476. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28620149 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akers K.G., Martinez-Canabal A., Restivo L., Yiu A.P., De Cristofaro A., Hsiang H.L., Wheeler A.L., Guskjolen A., Niibori Y., Shoji H., Ohira K., Richards B.A., Miyakawa T., Josselyn S.A., Frankland P.W. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 2014;344:598–602. - PubMed
-
- Bergami M., Masserdotti G., Temprana S.G., Motori E., Eriksson T.M., Gobel J., Yang S.M., Conzelmann K.K., Schinder A.F., Gotz M., Berninger B. A critical period for experience-dependent remodeling of adult-born neuron connectivity. Neuron. 2015;85:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Billuart P., Bienvenu T., Ronce N., Des Portes V., Vinet M.C., Zemni R., Carrie A., Beldjord C., Kahn A., Moraine C., Chelly J. Oligophrenin 1 encodes a rho-gap protein involved in X-linked mental retardation. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 1998;46:678. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

