TRPC1, Orai1, and STIM1 in SOCE: Friends in tight spaces
- PMID: 28089266
- PMCID: PMC5466534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.12.009
TRPC1, Orai1, and STIM1 in SOCE: Friends in tight spaces
Abstract
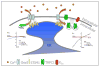
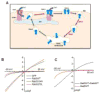
Store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) is a ubiquitous Ca2+ entry pathway that is activated in response to depletion of ER-Ca2+ stores and critically controls the regulation of physiological functions in miscellaneous cell types. The transient receptor potential canonical 1 (TRPC1) is the first member of the TRPC channel subfamily to be identified as a molecular component of SOCE. While TRPC1 has been shown to contribute to SOCE and regulate various functions in many cells, none of the reported TRPC1-mediated currents resembled ICRAC, the highly Ca2+-selective store-dependent current first identified in lymphocytes and mast cells. Almost a decade after the cloning of TRPC1 two proteins were identified as the primary components of the CRAC channel. The first, STIM1, is an ER-Ca2+ sensor protein involved in activating SOCE. The second, Orai1 is the pore-forming component of the CRAC channel. Co-expression of STIM1 and Orai1 generated robust ICRAC. Importantly, STIM1 was shown to also activate TRPC1 via its C-terminal polybasic domain, which is distinct from its Orai1-activating domain, SOAR. In addition, TRPC1 function critically depends on Orai1-mediated Ca2+ entry which triggers recruitment of TRPC1 into the plasma membrane where it is then activated by STIM1. TRPC1 and Orai1 form discrete STIM1-gated channels that generate distinct Ca2+ signals and regulate specific cellular functions. Surface expression of TRPC1 can be modulated by trafficking of the channel to and from the plasma membrane, resulting in changes to the phenotype of TRPC1-mediated current and [Ca2+]i signals. Thus, TRPC1 is activated downstream of Orai1 and modifies the initial [Ca2+]i signal generated by Orai1 following store depletion. This review will summarize the important findings that underlie the current concepts for activation and regulation of TRPC1, as well as its impact on cell function.
Keywords: Caveolin; ER-PM junctions; Lipid rafts; Orai1; SOCE; STIM1; TRPC.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Putney JW., Jr A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. 1986;7:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Cahalan MD, Lewis RS. Functional roles of ion channels in lymphocytes. Seminars in immunology. 1990;2:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Hoth M, Penner R. Depletion of inracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature. 1992;355:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Parekh AB, Fleig A, Penner R. The store-operated calcium current ICRAC: nonlinear activation by InsP3 and dissociation from calcium release. Cell. 1997;89:973–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

