MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition
- PMID: 28089889
- PMCID: PMC5310991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.12.005
MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition
Abstract
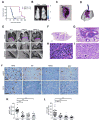
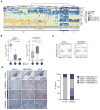
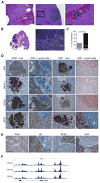
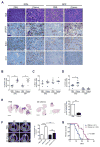
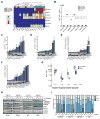
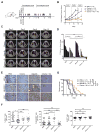
Loss of the tumor suppressors RB1 and TP53 and MYC amplification are frequent oncogenic events in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). We show that Myc expression cooperates with Rb1 and Trp53 loss in the mouse lung to promote aggressive, highly metastatic tumors, that are initially sensitive to chemotherapy followed by relapse, similar to human SCLC. Importantly, MYC drives a neuroendocrine-low "variant" subset of SCLC with high NEUROD1 expression corresponding to transcriptional profiles of human SCLC. Targeted drug screening reveals that SCLC with high MYC expression is vulnerable to Aurora kinase inhibition, which, combined with chemotherapy, strongly suppresses tumor progression and increases survival. These data identify molecular features for patient stratification and uncover a potential targeted treatment approach for MYC-driven SCLC.
Keywords: ASCL1; Aurora kinase inhibitor; MYC; NEUROD1; chemotherapy; genetically engineered mouse model; neuroendocrine; small-cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Brennan J, O'Connor T, Makuch RW, Simmons AM, Russell E, Linnoila RI, Phelps RM, Gazdar AF, Ihde DC, Johnson BE. myc family DNA amplification in 107 tumors and tumor cell lines from patients with small cell lung cancer treated with different combination chemotherapy regimens. Cancer Res. 1991;51:1708–1712. - PubMed
-
- Calbo J, van Montfort E, Proost N, van Drunen E, Beverloo HB, Meuwissen R, Berns A. A functional role for tumor cell heterogeneity in a mouse model of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:244–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

