A mast cell-ILC2-Th9 pathway promotes lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 28090087
- PMCID: PMC5241810
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14017
A mast cell-ILC2-Th9 pathway promotes lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis
Abstract
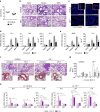
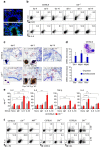
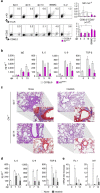
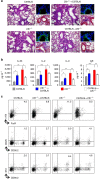
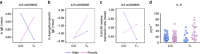
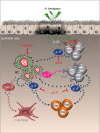
T helper 9 (Th9) cells contribute to lung inflammation and allergy as sources of interleukin-9 (IL-9). However, the mechanisms by which IL-9/Th9 mediate immunopathology in the lung are unknown. Here we report an IL-9-driven positive feedback loop that reinforces allergic inflammation. We show that IL-9 increases IL-2 production by mast cells, which leads to expansion of CD25+ type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and subsequent activation of Th9 cells. Blocking IL-9 or inhibiting CD117 (c-Kit) signalling counteracts the pathogenic effect of the described IL-9-mast cell-IL-2 signalling axis. Overproduction of IL-9 is observed in expectorates from cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, and a sex-specific variant of IL-9 is predictive of allergic reactions in female patients. Our results suggest that blocking IL-9 may be a therapeutic strategy to ameliorate inflammation associated with microbial colonization in the lung, and offers a plausible explanation for gender differences in clinical outcomes of patients with CF.
Figures

References
-
- Spits H. et al. Innate lymphoid cells–a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13, 145–149 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Roediger B. & Weninger W. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the regulation of immune responses. Adv. Immunol. 125, 111–154 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Halim T. Y., Krauss R. H., Sun A. C. & Takei F. Lung natural helper cells are a critical source of Th2 cell-type cytokines in protease allergen-induced airway inflammation. Immunity 36, 451–463 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

