Prevalence of obesity in Malta
- PMID: 28090352
- PMCID: PMC5192534
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.77
Prevalence of obesity in Malta
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a global epidemic with the Mediterranean island of Malta being no exception. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified Malta as one of the European countries with the highest obesity prevalence.
Method: A cross-sectional study was conducted (2014-2016) under the auspices of the University of Malta. The prevalence of overweight-obesity in Malta was calculated and then age stratified for comparisons with previous studies.
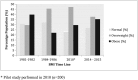
Results: The study identified 69.75% (95% CI: 68.32-71.18) of the Maltese population to be either overweight or obese. The men overweight/obese prevalence (76.28% 95% CI: 74.41-78.14) was statistically higher than that for women (63.06% 95% CI: 60.92-65.20) (p = 0.0001). Age stratification revealed that both genders had the highest overweight prevalence rates between 55 and 64 years (Men = 23.25% 95% CI: 20.43-26.33; Women = 24.68% 95% CI: 21.44-28.22). Men obesity prevalence rates were highest in the 35 to 44 years group (22.52% 95% CI: 19.65-25.68) while for women it was highest in the 55 to 64 years group (28.90%, 95% CI: 25.44-30.63).
Conclusion: Over a 35-year period, an overall decrease in the normal and overweight BMI categories occurred with an increase in the prevalence of obesity. An exception was observed in the women, where the prevalence of normal BMI increased over this time period. Also, it appears that while the total population obesity prevalence increased (for 2016), a percentage of the women have shifted from an obese to an overweight status.
Keywords: Epidemics; Malta; obesity; overweight.
Figures
References
-
- Brandt L, Erixon F. The prevalence and growth of obesity and obesity related illness in Europe. Eur Center Int Polit Econ (ECIPE) 2013.
-
- Lifshitz F, Lifshitz JZ. Globesity: the root causes of the obesity epidemic in the USA and now worldwide. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2014; 12: 17–34. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global Status Report on Non‐communicable diseases 2014—Chapter 7. Geneva, 2014.
-
- The World Bank . GDP per capita (current US$). Available: http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.PCAP.CD [Accessed 24th July 2016]
-
- Demographic Review 2013 . National Statistics Office Valletta 2015.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources