Soluble urokinase receptor (suPAR) predicts microalbuminuria in patients at risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 28091558
- PMCID: PMC5238426
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40627
Soluble urokinase receptor (suPAR) predicts microalbuminuria in patients at risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Early identification of patients at risk of developing diabetic nephropathy is essential. Elevated serum concentrations of soluble urokinase receptor (suPAR) associate with diabetes mellitus and predict onset and loss of renal function in chronic kidney disease. We hypothesize, that suPAR may be an early risk indicator for diabetic nephropathy, preceding microalbuminuria. The relationship of baseline suPAR and incident microalbuminuria was assessed in a prospective long-term cohort of subjects at increased risk for type 2 diabetes (TULIP, n = 258). Association with albuminuria at later stages of disease was studied in a cross-sectional cohort with manifest type 2 diabetes (ICEPHA, n = 266). A higher baseline suPAR was associated with an increased risk of new-onset microalbuminuria in subjects at risk for type 2 diabetes (hazard ratio 5.3 (95% CI 1.1-25.2, p = 0.03) for the highest vs. lowest suPAR quartile). The proportion of subjects with prediabetes at the end of observation was higher in subjects with new-onset microalbuminuria. suPAR consistently correlated with albuminuria in a separate cohort with manifest type 2 diabetes. Elevated baseline suPAR concentrations independently associate with new-onset microalbuminuria in subjects at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. suPAR may hence allow for earlier risk stratification than microalbuminuria.
Figures
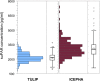

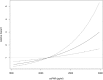
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 7th edition. http://www.diabetesatlas.org (Date of access: 18.10.2016) (2015).
-
- United States Renal Data System. Annual Data Report 2015. https://www.usrds.org/2015/view/Default.aspx (Date of access: 18.10.2016) (2015).
-
- ERA-EDTA Registry, Annual Report 2014. https://www.era-edta-reg.org/files/annualreports/pdf/AnnRep2014.pdf (Date of access: 18.10.2016) (2016).
-
- Gross J. L. et al.. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28, 164–176 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

