Effect of gravity and microgravity on intracranial pressure
- PMID: 28092926
- PMCID: PMC5350445
- DOI: 10.1113/JP273557
Effect of gravity and microgravity on intracranial pressure
Abstract
Key points: Astronauts have recently been discovered to have impaired vision, with a presentation that resembles syndromes of elevated intracranial pressure on Earth. Gravity has a profound effect on fluid distribution and pressure within the human circulation. In contrast to prevailing theory, we observed that microgravity reduces central venous and intracranial pressure. This being said, intracranial pressure is not reduced to the levels observed in the 90 deg seated upright posture on Earth. Thus, over 24 h in zero gravity, pressure in the brain is slightly above that observed on Earth, which may explain remodelling of the eye in astronauts.
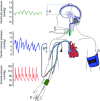
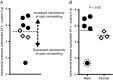
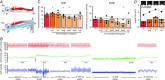
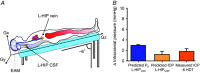
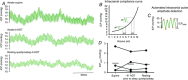
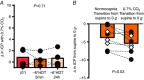
Abstract: Astronauts have recently been discovered to have impaired vision, with a presentation that resembles syndromes of elevated intracranial pressure (ICP). This syndrome is considered the most mission-critical medical problem identified in the past decade of manned spaceflight. We recruited five men and three women who had an Ommaya reservoir inserted for the delivery of prophylactic CNS chemotherapy, but were free of their malignant disease for at least 1 year. ICP was assessed by placing a fluid-filled 25 gauge butterfly needle into the Ommaya reservoir. Subjects were studied in the upright and supine position, during acute zero gravity (parabolic flight) and prolonged simulated microgravity (6 deg head-down tilt bedrest). ICP was lower when seated in the 90 deg upright posture compared to lying supine (seated, 4 ± 1 vs. supine, 15 ± 2 mmHg). Whilst lying in the supine posture, central venous pressure (supine, 7 ± 3 vs. microgravity, 4 ± 2 mmHg) and ICP (supine, 17 ± 2 vs. microgravity, 13 ± 2 mmHg) were reduced in acute zero gravity, although not to the levels observed in the 90 deg seated upright posture on Earth. Prolonged periods of simulated microgravity did not cause progressive elevations in ICP (supine, 15 ± 2 vs. 24 h head-down tilt, 15 ± 4 mmHg). Complete removal of gravity does not pathologically elevate ICP but does prevent the normal lowering of ICP when upright. These findings suggest the human brain is protected by the daily circadian cycles in regional ICPs, without which pathology may occur.
Keywords: bedrest; idiopathic intracranial hypertension; ocular remodeling; posture; space.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Intracranial pressure in outer space: preparing for the mission to Mars.J Physiol. 2017 Jul 15;595(14):4587-4588. doi: 10.1113/JP274315. Epub 2017 May 14. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28409841 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alexander DJ, Gibson CR, Hamilton DR MD, Lee SMC, Mader TH, Otto C, Oubre CM, Pass AF, Platts SH, Scott JM, Smith SM, Stenger MB, Westby CM & Zanello SB (2012). Risk of spaceflight‐induced intracranial hypertension and vision alterations. Available at: https://humanresearchroadmap.nasa.gov/evidence/reports/viip.pdf
-
- Anderson AP, Swan JG, Phillips SD, Knaus DA, Kattamis NT, Toutain‐Kidd CM, Zegans ME, Fellows AM & Buckey JC (2016). Acute effects of changes to the gravitational vector on the eye. J Appl Physiol (1985) 120, 939–946. - PubMed
-
- Buckey JC, Gaffney FA, Lane LD, Levine BD, Watenpaugh DE & Blomqvist CG (1993). Central venous pressure in space. N Engl J Med 328, 1853–1854. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DF, Grimby G, Jones DA & Edwards RH (1979). Perception of effort in isometric and dynamic muscular contraction. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 41, 173–180. - PubMed
-
- Davson H, Domer FR & Hollingsworth JR (1973). The mechanism of drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain 96, 329–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

