Establishing between-session reliability of TMS-conditioned soleus H-reflexes
- PMID: 28093306
- PMCID: PMC5315025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.032
Establishing between-session reliability of TMS-conditioned soleus H-reflexes
Abstract
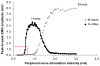
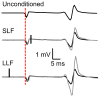
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) of the primary motor cortex (M1) can be used to evaluate descending corticomotor influences on spinal reflex excitability through modulation of the Hoffman reflex (H-reflex). The purpose of this study was to characterize between-session reliability of cortical, spinal, and cortical-conditioned spinal excitability measures collected from the soleus muscle. Thirteen able-bodied young adult participants were tested over four sessions. Intraclass correlation coefficients were calculated to quantify between-session reliability of active motor threshold (AMT), unconditioned H-reflexes (expressed as a percentage of Mmax), and conditioned H-reflexes using short-latency facilitation (SLF) and long-latency facilitation (LLF). Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to assess associations between H-reflex facilitation and unconditioned H-reflex amplitude. Between-session reliability for SLF (ICC=0.71) was higher than for LLF (ICC=0.45), was excellent for AMT (ICC=0.95), and was moderate for unconditioned H-reflexes (ICC=0.63). Our results suggest moderate-to-good reliability of SLF and LLF to evaluate cortical influences on spinal reflex excitability across multiple testing sessions in able-bodied individuals.
Keywords: Corticospinal excitability; Facilitation; H-reflex; Reliability; TMS; TMS-conditioning.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spinal inhibition of descending command to soleus motoneurons is removed prior to dorsiflexion.J Physiol. 2011 Dec 1;589(Pt 23):5819-31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.214387. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21986208 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Latency of changes in spinal motoneuron excitability evoked by transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in spinal cord injured individuals.Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998 Aug;109(4):297-303. doi: 10.1016/s0924-980x(98)00021-6. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9751291
-
Reliability of the TMS-conditioned monosynaptic reflex in the flexor carpi radialis muscle.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Feb 6;745:135622. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135622. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33421494
-
Cerebellar TMS Induces Motor Responses Mediating Modulation of Spinal Excitability: A Literature Review.Brain Sci. 2023 Mar 23;13(4):531. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040531. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Spinal and Corticospinal Excitability in Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2019 Jul 16;8(7):1037. doi: 10.3390/jcm8071037. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31315231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of Convergent Sensorimotor Inputs Within Spinal Reflex Circuits in Healthy Adults.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Nov 26;14:592013. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.592013. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33324184 Free PMC article.
-
The use of transcranial magnetic stimulation to evaluate cortical excitability of lower limb musculature: Challenges and opportunities.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2018;36(3):333-348. doi: 10.3233/RNN-170801. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29758954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing the corticomotor connectivity of the bilateral ankle muscles during rest and isometric contraction in healthy adults.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018 Aug;41:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2018.04.009. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2018. PMID: 29715530 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Profile of Descending Cortical Modulation of Spinal Excitability: Group and Individual-Specific Effects.Front Integr Neurosci. 2022 Jan 7;15:777741. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2021.777741. eCollection 2021. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35197831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman DG. Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman & Hall; London: 1991.
-
- Burke D, Adams RW, Skuse NF. The effects of voluntary contraction on the H reflex of human limb muscles. Brain. 1989;112(Pt 2):417–433. - PubMed
-
- Cacchio A, Cimini N, Alosi P, Santilli V, Marrelli A. Reliability of transcranial magnetic stimulation-related measurements of tibialis anterior muscle in healthy subjects. Clinical neurophysiology: official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2009;120:414–419. - PubMed
-
- Carroll TJ, Riek S, Carson RG. Reliability of the input-output properties of the cortico-spinal pathway obtained from transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation. J Neurosci Methods. 2001;112:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Castaingts V, Martin A, Van Hoecke J, Perot C. Neuromuscular efficiency of the triceps surae in induced and voluntary contractions: morning and evening evaluations. Chronobiol Int. 2004;21:631–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

