Association of Body Mass Index with DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Blood Cells and Relations to Cardiometabolic Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Approach
- PMID: 28095459
- PMCID: PMC5240936
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002215
Association of Body Mass Index with DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Blood Cells and Relations to Cardiometabolic Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Approach
Abstract
Background: The link between DNA methylation, obesity, and adiposity-related diseases in the general population remains uncertain.
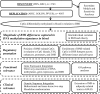
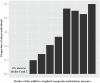
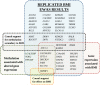
Methods and findings: We conducted an association study of body mass index (BMI) and differential methylation for over 400,000 CpGs assayed by microarray in whole-blood-derived DNA from 3,743 participants in the Framingham Heart Study and the Lothian Birth Cohorts, with independent replication in three external cohorts of 4,055 participants. We examined variations in whole blood gene expression and conducted Mendelian randomization analyses to investigate the functional and clinical relevance of the findings. We identified novel and previously reported BMI-related differential methylation at 83 CpGs that replicated across cohorts; BMI-related differential methylation was associated with concurrent changes in the expression of genes in lipid metabolism pathways. Genetic instrumental variable analysis of alterations in methylation at one of the 83 replicated CpGs, cg11024682 (intronic to sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 [SREBF1]), demonstrated links to BMI, adiposity-related traits, and coronary artery disease. Independent genetic instruments for expression of SREBF1 supported the findings linking methylation to adiposity and cardiometabolic disease. Methylation at a substantial proportion (16 of 83) of the identified loci was found to be secondary to differences in BMI. However, the cross-sectional nature of the data limits definitive causal determination.
Conclusions: We present robust associations of BMI with differential DNA methylation at numerous loci in blood cells. BMI-related DNA methylation and gene expression provide mechanistic insights into the relationship between DNA methylation, obesity, and adiposity-related diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
JS is an advisory board member for Itrim. CF is now an employee of Merck, but was not an employee when the work was conducted. EI is a scientific advisor and consultant for Precision Wellness, Inc. and scientific advisor for Cellink for work unrelated to this paper. IJD has research grants from Age UK and the UK Medical Research Council.
Figures
References
-
- Lu Y, Hajifathalian K, Ezzati M, Woodward M, Rimm EB, Danaei G. Metabolic mediators of the effects of body-mass index, overweight, and obesity on coronary heart disease and stroke: a pooled analysis of 97 prospective cohorts with 1.8 million participants. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):970–83. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61836-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL104135/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG042187/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072524/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 CA196375/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL135313/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

