The Burden of Mental Disorders in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 1990-2013
- PMID: 28095477
- PMCID: PMC5240956
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169575
The Burden of Mental Disorders in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 1990-2013
Abstract
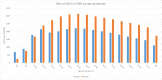
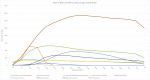
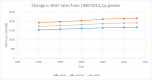
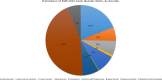
The Eastern Mediterranean Region (EMR) is witnessing an increase in chronic disorders, including mental illness. With ongoing unrest, this is expected to rise. This is the first study to quantify the burden of mental disorders in the EMR. We used data from the Global Burden of Disease study (GBD) 2013. DALYs (disability-adjusted life years) allow assessment of both premature mortality (years of life lost-YLLs) and nonfatal outcomes (years lived with disability-YLDs). DALYs are computed by adding YLLs and YLDs for each age-sex-country group. In 2013, mental disorders contributed to 5.6% of the total disease burden in the EMR (1894 DALYS/100,000 population): 2519 DALYS/100,000 (2590/100,000 males, 2426/100,000 females) in high-income countries, 1884 DALYS/100,000 (1618/100,000 males, 2157/100,000 females) in middle-income countries, 1607 DALYS/100,000 (1500/100,000 males, 1717/100,000 females) in low-income countries. Females had a greater proportion of burden due to mental disorders than did males of equivalent ages, except for those under 15 years of age. The highest proportion of DALYs occurred in the 25-49 age group, with a peak in the 35-39 years age group (5344 DALYs/100,000). The burden of mental disorders in EMR increased from 1726 DALYs/100,000 in 1990 to 1912 DALYs/100,000 in 2013 (10.8% increase). Within the mental disorders group in EMR, depressive disorders accounted for most DALYs, followed by anxiety disorders. Among EMR countries, Palestine had the largest burden of mental disorders. Nearly all EMR countries had a higher mental disorder burden compared to the global level. Our findings call for EMR ministries of health to increase provision of mental health services and to address the stigma of mental illness. Moreover, our results showing the accelerating burden of mental health are alarming as the region is seeing an increased level of instability. Indeed, mental health problems, if not properly addressed, will lead to an increased burden of diseases in the region.
Conflict of interest statement
We would like to declare the following commercial affiliations: Dr. Anwar Rafay is employed by Contech International health consultants. Syed Danish Ali is employed by SIR Consultants. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
-
- World Health O. Mental Health Gap Action Programme: scaling up care for mental, neurological and substance use disorders World Health Organisation (WHO); 2008. - PubMed
-
- World Health O. The World Health Report 2001 Mental Health: New Understanding, New Hope: World Health Organization (WHO); 2001.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

