Functional role and therapeutic targeting of p21-activated kinase 4 in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 28096095
- PMCID: PMC5399480
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-06-724831
Functional role and therapeutic targeting of p21-activated kinase 4 in multiple myeloma
Abstract
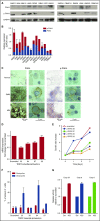
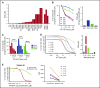
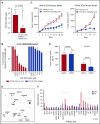
Dysregulated oncogenic serine/threonine kinases play a pathological role in diverse forms of malignancies, including multiple myeloma (MM), and thus represent potential therapeutic targets. Here, we evaluated the biological and functional role of p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) and its potential as a new target in MM for clinical applications. PAK4 promoted MM cell growth and survival via activation of MM survival signaling pathways, including the MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Furthermore, treatment with orally bioavailable PAK4 allosteric modulator (KPT-9274) significantly impacted MM cell growth and survival in a large panel of MM cell lines and primary MM cells alone and in the presence of bone marrow microenvironment. Intriguingly, we have identified FGFR3 as a novel binding partner of PAK4 and observed significant activity of KPT-9274 against t(4;14)-positive MM cells. This set of data supports PAK4 as an oncogene in myeloma and provide the rationale for the clinical evaluation of PAK4 modulator in myeloma.
Figures




Comment in
-
Multiple myeloma cells sent "PAKing"!Blood. 2017 Apr 20;129(16):2208-2209. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-02-764662. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28428234 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, Richardson PG, Anderson KC. Understanding multiple myeloma pathogenesis in the bone marrow to identify new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(8):585-598. - PubMed
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(11):1046-1060. - PubMed
-
- Mateos MV, Ocio EM, Paiva B, et al. Treatment for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma in 2015. Blood Rev. 2015;29(6):387-403. - PubMed
-
- Dan C, Kelly A, Bernard O, Minden A. Cytoskeletal changes regulated by the PAK4 serine/threonine kinase are mediated by LIM kinase 1 and cofilin. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(34):32115-32121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

