TORC1-dependent sumoylation of Rpc82 promotes RNA polymerase III assembly and activity
- PMID: 28096404
- PMCID: PMC5293095
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1615093114
TORC1-dependent sumoylation of Rpc82 promotes RNA polymerase III assembly and activity
Abstract
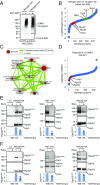
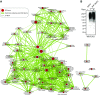
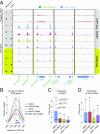
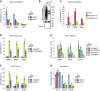
Maintaining cellular homeostasis under changing nutrient conditions is essential for the growth and development of all organisms. The mechanisms that maintain homeostasis upon loss of nutrient supply are not well understood. By mapping the SUMO proteome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we discovered a specific set of differentially sumoylated proteins mainly involved in transcription. RNA polymerase III (RNAPIII) components, including Rpc53, Rpc82, and Ret1, are particularly prominent nutrient-dependent SUMO targets. Nitrogen starvation, as well as direct inhibition of the master nutrient response regulator target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1), results in rapid desumoylation of these proteins, which is reflected by loss of SUMO at tRNA genes. TORC1-dependent sumoylation of Rpc82 in particular is required for robust tRNA transcription. Mechanistically, sumoylation of Rpc82 is important for assembly of the RNAPIII holoenzyme and recruitment of Rpc82 to tRNA genes. In conclusion, our data show that TORC1-dependent sumoylation of Rpc82 bolsters the transcriptional capacity of RNAPIII under optimal growth conditions.
Keywords: RNA polymerase III; Sumo; TORC1; tRNA; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
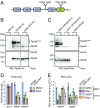
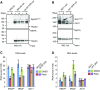


References
-
- Warner JR. The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24(11):437–440. - PubMed
-
- Desai N, et al. Two steps in Maf1-dependent repression of transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(8):6455–6462. - PubMed
-
- Vannini A, et al. Molecular basis of RNA polymerase III transcription repression by Maf1. Cell. 2010;143(1):59–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

