Genomic analysis and clinical management of adolescent cutaneous melanoma
- PMID: 28097802
- PMCID: PMC5435926
- DOI: 10.1111/pcmr.12574
Genomic analysis and clinical management of adolescent cutaneous melanoma
Abstract
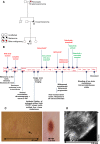
Melanoma in young children is rare; however, its incidence in adolescents and young adults is rising. We describe the clinical course of a 15-year-old female diagnosed with AJCC stage IB non-ulcerated primary melanoma, who died from metastatic disease 4 years after diagnosis despite three lines of modern systemic therapy. We also present the complete genomic profile of her tumour and compare this to a further series of 13 adolescent melanomas and 275 adult cutaneous melanomas. A somatic BRAFV600E mutation and a high mutational load equivalent to that found in adult melanoma and composed primarily of C>T mutations were observed. A germline genomic analysis alongside a series of 23 children and adolescents with melanoma revealed no mutations in known germline melanoma-predisposing genes. Adolescent melanomas appear to have genomes that are as complex as those arising in adulthood and their clinical course can, as with adults, be unpredictable.
Keywords: BRAF mutation; adolescent melanoma; germline mutation; immunotherapy; ultraviolet radiation.
© 2017 The Authors. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Austin, M.T. , Xing, Y. , Hayes‐Jordan, A.A. , Lally, K.P. , and Cormier, J.N. (2013). Melanoma incidence rises for children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review of pediatric melanoma in the United States. J. Pediatr. Surg. 48, 2207–2213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

