Signalling pathways involved in hypoxia-induced renal fibrosis
- PMID: 28097825
- PMCID: PMC5487923
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13060
Signalling pathways involved in hypoxia-induced renal fibrosis
Abstract
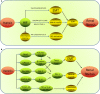
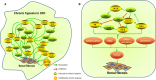
Renal fibrosis is the common pathological hallmark of progressive chronic kidney disease (CKD) with diverse aetiologies. Recent researches have highlighted the critical role of hypoxia during the development of renal fibrosis as a final common pathway in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), which joints the scientist's attention recently to exploit the molecular mechanism underlying hypoxia-induced renal fibrogenesis. The scaring formation is a multilayered cellular response and involves the regulation of multiple hypoxia-inducible signalling pathways and complex interactive networks. Therefore, this review will focus on the signalling pathways involved in hypoxia-induced pathogenesis of interstitial fibrosis, including pathways mediated by HIF, TGF-β, Notch, PKC/ERK, PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, Ang II/ROS and microRNAs. Roles of molecules such as IL-6, IL-18, KIM-1 and ADO are also reviewed. A comprehensive understanding of the roles that these hypoxia-responsive signalling pathways and molecules play in the context of renal fibrosis will provide a foundation towards revealing the underlying mechanisms of progression of CKD and identifying novel therapeutic targets. In the future, promising new effective therapy against hypoxic effects may be successfully translated into the clinic to alleviate renal fibrosis and inhibit the progression of CKD.
Keywords: Signalling pathways; hypoxia; renal fibrosis.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Fine LG, Bandyopadhay D, Norman JT. Is there a common mechanism for the progression of different types of renal diseases other than proteinuria? Towards the unifying theme of chronic hypoxia Kidney Int Suppl. 2000; 75: S22–6. - PubMed
-
- Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: a final common pathway to end‐stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17: 17–25. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T. Expanding roles of the hypoxia‐response network in chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016; 20: 835–44. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T, Nangaku M. The role of hypoxia, increased oxygen consumption, and hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1 alpha in progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010; 19: 43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

