Morroniside, a secoiridoid glycoside from Cornus officinalis, attenuates neuropathic pain by activation of spinal glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors
- PMID: 28098360
- PMCID: PMC5345663
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13720
Morroniside, a secoiridoid glycoside from Cornus officinalis, attenuates neuropathic pain by activation of spinal glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors
Abstract
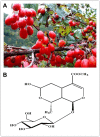
Background and purpose: Iridoid glycosides containing the double bond scaffold of cyclopentapyran are reversible and orthosteric agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors and exert anti-nociceptive and neuroprotective actions. Morroniside, derived from the medicinal herb Cornus officinalis, is an atypical secoiridoid containing a six-membered cyclic inner ether fragment. Here we investigated whether morroniside was an orthosteric GLP-1 receptor agonist and had anti-hypersensitivity activities in a model of neuropathic pain.
Experimental approach: We used a model of neuropathic pain, induced by tight ligation of L5/L6 spinal nerves in rats. Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage was also assayed in N9 microglial cells and human HEK293 cells stably expressing GLP-1 receptors.
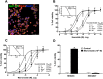
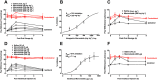
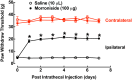
Key results: Morroniside protected against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in N9 microglial and HEK293 cells that expressed mouse or human GLP-1 receptors, but not in HEK293T cells without GLP-1 receptors. The GLP-1 receptor orthosteric antagonist exendin(9-39) also concentration-dependently shifted the concentration-protective response curves of morroniside and exenatide to the right without affecting maximal protection, with similar pA2 values. Furthermore, morroniside given by oral gavage or intrathecally in neuropathic rats dose-dependently attenuated mechanical allodynia, with comparable Emax values and ED50 s of 335 mg·kg-1 and 7.1 μg and completely blocked thermal hyperalgesia. Daily intrathecal injections of morroniside over 7 days did not induce anti-allodynic tolerance. Pretreatment with intrathecal exendin(9-39) completely blocked systemic and intrathecal morroniside-induced mechanical anti-allodynia.
Conclusion and implications: Our data demonstrated that morroniside was an orthosteric agonist of GLP-1 receptors and produced antihypersensitivity in a neuropathic pain model by activation of spinal GLP-1 receptors.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Ai HX, Wang W, Sun FL, Huang WT, An Y, Li L (2008). Morroniside inhibits H2O2‐induced apoptosis in cultured nerve cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 33: 2109–2112. - PubMed
-
- Baggio LL, Drucker DJ (2007). Biology of incretins: GLP‐1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 132: 2131–2157. - PubMed
-
- Collett BJ (1998). Opioid tolerance: the clinical perspective. Br J Anaesth 81: 58–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

