Motuporamine Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents and Antibiotic Enhancers against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
- PMID: 28098416
- PMCID: PMC5299527
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201600532
Motuporamine Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents and Antibiotic Enhancers against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
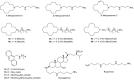
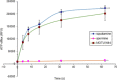
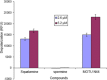
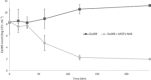
Dihydromotuporamine C and its derivatives were evaluated for their in vitro antimicrobial activities and antibiotic enhancement properties against Gram-negative bacteria and clinical isolates. The mechanism of action of one of these derivatives, MOTU-N44, was investigated against Enterobacter aerogenes by using fluorescent dyes to evaluate outer-membrane depolarization and permeabilization. Its efficiency correlated with inhibition of dye transport, thus suggesting that these molecules inhibit drug transporters by de-energization of the efflux pump rather than by direct interaction of the molecule with the pump. This suggests that depowering the efflux pump provides another strategy to address antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial agents; bacterial resistance; membranes; motuporamine; polyamine derivatives.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures

References
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance WHO, 2014, http://www.who.int/drugresistance/documents/surveillancereport/en/.
-
- Fernandes P., Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1497–1503. - PubMed
-
- Pop-Vicas A. E., D'Agata E. M. C., Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1792–1798. - PubMed
-
- Jennings M. C., Minbiole K. P. C., Wuest W. M., ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 288–303. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

