Penduliflaworosin, a Diterpenoid from Croton crassifolius, Exerts Anti-Angiogenic Effect via VEGF Receptor-2 Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 28098802
- PMCID: PMC6155893
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22010126
Penduliflaworosin, a Diterpenoid from Croton crassifolius, Exerts Anti-Angiogenic Effect via VEGF Receptor-2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
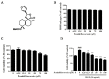
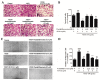
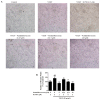
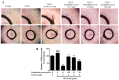
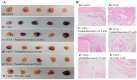
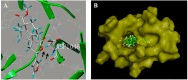
Anti-angiogenesis targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) has been considered as an important strategy for cancer therapy. Penduliflaworosin is a diterpenoid isolated from the plant Croton crassifolius. Our previous study showed that this diterpenoid possesses strong anti-angiogenic activity by inhibiting vessel formation in zebrafish. This study was conducted to further investigate the anti-angiogenic activity and mechanism of penduliflaworosin. Results revealed that penduliflaworosin significantly inhibited VEGF-induced angiogenesis processes including proliferation, invasion, migration, and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Moreover, it notably inhibited VEGF-induced sprout formation of aortic rings and blocked VEGF-induced vessel formation in mice. Western blotting studies showed that penduliflaworosin inhibited phosphorylation of the VEGF receptor-2 and its downstream signaling mediators in HUVECs, suggesting that the anti-angiogenic activity was due to an interference with the VEGF/VEGF receptor-2 pathway. In addition, molecular docking simulation indicated that penduliflaworosin could form hydrogen bonds within the ATP-binding region of the VEGF receptor-2 kinase unit. Finally, cytotoxicity assay showed that penduliflaworosin possessed little toxicity toward both cancer and normal cells. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that penduliflaworosin exerts its anti-angiogenic effect via the VEGF receptor-2 signaling pathway. The anti-angiogenic property and low cytotoxicity of penduliflaworosin suggest that it may be useful in cancer treatments.
Keywords: VEGF receptor-2; anti-angiogenesis; penduliflaworosin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Michael P., Herman I.M. Mechanisms of normal and tumor-derived angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell. Physiol. 2002;282:C947–C970. - PubMed
-
- David B., Harold W. Targeting the growth factors and angiogenesis pathways: Small molecules in solid tumors. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011;103:574–586. - PubMed
-
- Fyfe G.A., Hurwitz H., Fehrenbacher L., Cartwright T., Hainsworth J., Heim W., Berlin J., Kabbinavar F., Holmgren E., Novotny W. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan/5-FU/leucovorin for treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer results in survival benefit in all pre-specified patient subgroups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004;22:3617.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

