Systolic peak foot-to-apex time interval, a novel oscillometric technique for systolic blood pressure measurement
- PMID: 28099195
- PMCID: PMC5378056
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001252
Systolic peak foot-to-apex time interval, a novel oscillometric technique for systolic blood pressure measurement
Abstract
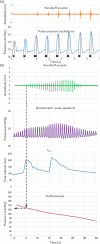
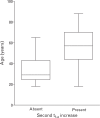
Background: Noninvasive blood pressure (BP) measurement is essential for the study of human physiology but automatic oscillometric devices only estimate SBP and DBP using various, undisclosed algorithms, precluding standardization and interchangeability. We propose a novel approach by tracking, during pneumatic cuff deflation, the time interval from the foot to the apex of the systolic peak of the oscillometric signal, which reaches a maximum concomitant with the first Korotkoff sound.
Method: In 145 study participants and patients (group 1), we measured the systolic brachial artery blood pressure by Korotkoff sound recording, conventional oscillometry, and our fully automated systolic peak foot-to-apex time interval (SFATI) technique. In 35 other patients (group 2), we compared SFATI with intra-arterial measurement.
Results: In group 1, the concordance correlation coefficient was 0.989 and 0.984 between SFATI and Korotkoff sounds, 0.884 and 0.917 between oscillometry and Korotkoff sounds, and 0.882 and 0.919 between SFATI and oscillometry, respectively, on the left and right arm. In group 2, it was 0.72 between SFATI and intra-arterial measurement, 0.67 between oscillometry and intra-arterial measurement, and 0.92 between SFATI and Korotkoff sounds. In 40 study participants, the reproducibility study yielded a concordance coefficient of 0.95 for SFATI and 0.94 for Korotkoff sounds.
Conclusion: SFATI BP measurement shows an excellent concordance with the auscultatory technique, offering a major improvement over current oscillometric techniques and allowing standardization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct Determination rather than Oscillometric Estimation of Systolic Blood Pressure in Patients with Severe Chronic Kidney Disease.Am J Nephrol. 2022;53(1):41-49. doi: 10.1159/000520996. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Am J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35021175
-
Variation of the Korotkoff Stethoscope Sounds During Blood Pressure Measurement: Analysis Using a Convolutional Neural Network.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017 Nov;21(6):1593-1598. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2703115. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017. PMID: 29136608
-
Non-invasive determination of instantaneous brachial blood flow using the oscillometric method.Biomed Tech (Berl). 2009 Aug;54(4):171-7. doi: 10.1515/BMT.2009.020. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19807282
-
From Korotkoff and Marey to automatic non-invasive oscillometric blood pressure measurement: does easiness come with reliability?Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13(2):179-89. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2016.1128821. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016. PMID: 26641026 Review.
-
Blood pressure measurement: retrospective and prospective views.Am J Hypertens. 2011 Jun;24(6):628-34. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.22. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Am J Hypertens. 2011. PMID: 21350431 Review.
Cited by
-
Applicability of electronic sphygmomanometer use in high-altitude areas according to the AAMI/ESH/ISO collaboration statement.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 8;10:1257444. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1257444. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38259316 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Blood Pressure in Humans: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Hypertension. 2019 May;73(5):e35-e66. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000087. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 30827125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Campbell NR, Berbari AE, Cloutier L, Gelfer M, Kenerson JG, Khalsa TK, et al. Policy statement of the world hypertension league on noninvasive blood pressure measurement devices and blood pressure measurement in the clinical or community setting. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2014; 16:320–322. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Daskalopoulou SS, Rabi DM, Zarnke KB, Dasgupta K, Nerenberg K, Cloutier L, et al. The 2015 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for blood pressure measurement, diagnosis, assessment of risk, prevention, and treatment of hypertension. Can J Cardiol 2015; 31:549–568. - PubMed
-
- Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, Mann S, Lindholm LH, Kenerson JG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community: a statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2014; 16:14–26. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Brien E, Atkins N, Stergiou G, Karpettas N, Parati G, Asmar R, et al. Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring of the European Society of Hypertension European Society of Hypertension International Protocol revision 2010 for the validation of blood pressure measuring devices in adults. Blood Press Monit 2010; 15:23–38. - PubMed
-
- Stergiou GS, Karpettas N, Atkins N, O’Brien E. European Society of Hypertension International Protocol for the validation of blood pressure monitors: a critical review of its application and rationale for revision. Blood Press Monit 2010; 15:39–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

