Replication Study: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc
- PMID: 28100400
- PMCID: PMC5245966
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.21253
Replication Study: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc
Erratum in
-
Correction: Replication Study: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc.Elife. 2018 Jan 8;7:e34572. doi: 10.7554/eLife.34572. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29309031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
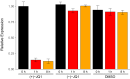
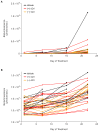
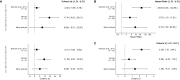
In 2015, as part of the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology, we published a Registered Report (Kandela et al., 2015) that described how we intended to replicate selected experiments from the paper "BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc" (Delmore et al., 2011). Here we report the results of those experiments. We found that treatment of human multiple myeloma (MM) cells with the small-molecular inhibitor of BET bromodomains, (+)-JQ1, selectively downregulated MYC transcription, which is similar to what was reported in the original study (Figure 3B; Delmore et al., 2011). Efficacy of (+)-JQ1 was evaluated in an orthotopically xenografted model of MM. Overall survival was increased in (+)-JQ1 treated mice compared to vehicle control, similar to the original study (Figure 7E; Delmore et al., 2011). Tumor burden, as determined by bioluminescence, was decreased in (+)-JQ1 treated mice compared to vehicle control; however, while the effect was in the same direction as the original study (Figure 7C-D; Delmore et al., 2011), it was not statistically significant. The opportunity to detect a statistically significant difference was limited though, due to the higher rate of early death in the control group, and increased overall survival in (+)-JQ1 treated mice before the pre-specified tumor burden analysis endpoint. Additionally, we evaluated the (-)-JQ1 enantiomer that is structurally incapable of inhibiting BET bromodomains, which resulted in a minimal impact on MYC transcription, but did not result in a statistically significant difference in tumor burden or survival distributions compared to treatment with (+)-JQ1. Finally, we report meta-analyses for each result.
Keywords: Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology; bromodomain inhibitor; cancer biology; human; metascience; mouse; myeloma; replication; reproducibility.
Conflict of interest statement
FA: Developmental Therapeutics Core is a Science Exchange associated lab. IK: Developmental Therapeutics Core is a Science Exchange associated lab. CM: Developmental Therapeutics Core is a Science Exchange associated lab. RP:CB: EI, NP: Employed by and hold shares in Science Exchange Inc.The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Comment in
-
Small molecules remain on target for c-Myc.Elife. 2017 Jan 19;6:e22915. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22915. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28100396 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Registered report: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc.Elife. 2015 Jun 25;4:e07072. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07072. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26111384 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules remain on target for c-Myc.Elife. 2017 Jan 19;6:e22915. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22915. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28100396 Free PMC article.
-
The Bromodomain Inhibitor JQ1 and the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Panobinostat Synergistically Reduce N-Myc Expression and Induce Anticancer Effects.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 May 15;22(10):2534-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1666. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26733615
-
BET bromodomain inhibition of MYC-amplified medulloblastoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 15;20(4):912-25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2281. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24297863 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MYC in multiple myeloma.Leukemia. 2018 Jun;32(6):1295-1306. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0036-x. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Leukemia. 2018. PMID: 29467490 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges for assessing replicability in preclinical cancer biology.Elife. 2021 Dec 7;10:e67995. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67995. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34874008 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel coumarin derivatives as potent and orally bioavailable BRD4 inhibitors based on scaffold hopping.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):808-817. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1587417. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30879350 Free PMC article.
-
Can cancer researchers accurately judge whether preclinical reports will reproduce?PLoS Biol. 2017 Jun 29;15(6):e2002212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2002212. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28662052 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4 inhibition sensitizes aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas to PI3Kδ inhibitors by suppressing PI3K reactivation and c-MYC expression.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):215-235. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33520370 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer reproducibility project releases first results.Nature. 2017 Jan 18;541(7637):269-270. doi: 10.1038/541269a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28102271 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aird F, Kandela I, Mantis C, Iorns E, Denis A, Williams SR, Perfito N, Errington TM. Study 19: replication of delmore et al., 2011 (Cell) Open Science Framework. 2016 doi: 10.17605/OSF.IO/7ZQXP. - DOI
-
- Amorim S, Stathis A, Gleeson M, Iyengar S, Magarotto V, Leleu X, Morschhauser F, Karlin L, Broussais F, Rezai K, Herait P, Kahatt C, Lokiec F, Salles G, Facon T, Palumbo A, Cunningham D, Zucca E, Thieblemont C. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: a dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. The Lancet Haematology. 2016;3:e196–e204. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(16)00021-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Asangani IA, Wilder-Romans K, Dommeti VL, Krishnamurthy PM, Apel IJ, Escara-Wilke J, Plymate SR, Navone NM, Wang S, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM. BET Bromodomain Inhibitors enhance efficacy and disrupt resistance to AR antagonists in the treatment of prostate cancer. Molecular Cancer Research. 2016;14:324–331. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azab AK, Runnels JM, Pitsillides C, Moreau AS, Azab F, Leleu X, Jia X, Wright R, Ospina B, Carlson AL, Alt C, Burwick N, Roccaro AM, Ngo HT, Farag M, Melhem MR, Sacco A, Munshi NC, Hideshima T, Rollins BJ, Anderson KC, Kung AL, Lin CP, Ghobrial IM. CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 disrupts the interaction of multiple myeloma cells with the bone marrow microenvironment and enhances their sensitivity to therapy. Blood. 2009;113:4341–4351. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-10-186668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

