Dynamic Modulation of Expression of Lentiviral Restriction Factors in Primary CD4+ T Cells following Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
- PMID: 28100613
- PMCID: PMC5355611
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02189-16
Dynamic Modulation of Expression of Lentiviral Restriction Factors in Primary CD4+ T Cells following Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
Abstract
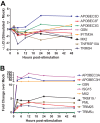
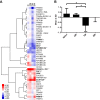
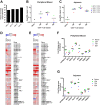
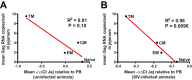
Although multiple restriction factors have been shown to inhibit HIV/SIV replication, little is known about their expression in vivo Expression of 45 confirmed and putative HIV/SIV restriction factors was analyzed in CD4+ T cells from peripheral blood and the jejunum in rhesus macaques, revealing distinct expression patterns in naive and memory subsets. In both peripheral blood and the jejunum, memory CD4+ T cells expressed higher levels of multiple restriction factors compared to naive cells. However, relative to their expression in peripheral blood CD4+ T cells, jejunal CCR5+ CD4+ T cells exhibited significantly lower expression of multiple restriction factors, including APOBEC3G, MX2, and TRIM25, which may contribute to the exquisite susceptibility of these cells to SIV infection. In vitro stimulation with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies or type I interferon resulted in upregulation of distinct subsets of multiple restriction factors. After infection of rhesus macaques with SIVmac239, the expression of most confirmed and putative restriction factors substantially increased in all CD4+ T cell memory subsets at the peak of acute infection. Jejunal CCR5+ CD4+ T cells exhibited the highest levels of SIV RNA, corresponding to the lower restriction factor expression in this subset relative to peripheral blood prior to infection. These results illustrate the dynamic modulation of confirmed and putative restriction factor expression by memory differentiation, stimulation, tissue microenvironment and SIV infection and suggest that differential expression of restriction factors may play a key role in modulating the susceptibility of different populations of CD4+ T cells to lentiviral infection.IMPORTANCE Restriction factors are genes that have evolved to provide intrinsic defense against viruses. HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) target CD4+ T cells. The baseline level of expression in vivo and degree to which expression of restriction factors is modulated by conditions such as CD4+ T cell differentiation, stimulation, tissue location, or SIV infection are currently poorly understood. We measured the expression of 45 confirmed and putative restriction factors in primary CD4+ T cells from rhesus macaques under various conditions, finding dynamic changes in each state. Most dramatically, in acute SIV infection, the expression of almost all target genes analyzed increased. These are the first measurements of many of these confirmed and putative restriction factors in primary cells or during the early events after SIV infection and suggest that the level of expression of restriction factors may contribute to the differential susceptibility of CD4+ T cells to SIV infection.
Keywords: CD4+ T lymphocytes; gut-associated lymphoid tissue; interferon-stimulated genes; restriction factors; simian immunodeficiency virus.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Stremlau M, Perron M, Lee M, Li Y, Song B, Javanbakht H, Diaz-Griffero F, Anderson DJ, Sundquist WI, Sodroski J. 2006. Specific recognition and accelerated uncoating of retroviral capsids by the TRIM5α restriction factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:5514–5519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509996103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Damme N, Goff D, Katsura C, Jorgenson RL, Mitchell R, Johnson MC, Stephens EB, Guatelli J. 2008. The interferon-induced protein BST-2 restricts HIV-1 release and is downregulated from the cell surface by the viral Vpu protein. Cell Host Microbe 3:245–252. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.03.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

