Compensatory Activation of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inhibition of GABA Release in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Inflammatory Pain
- PMID: 28100744
- PMCID: PMC5242409
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1310-16.2016
Compensatory Activation of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inhibition of GABA Release in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla in Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
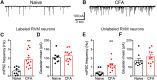
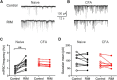
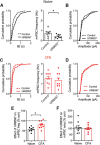
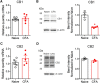
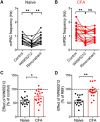
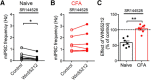
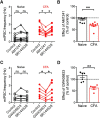
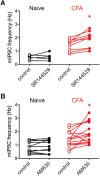
The rostral ventromedial medulla (RVM) is a relay in the descending pain modulatory system and an important site of endocannabinoid modulation of pain. Endocannabinoids inhibit GABA release in the RVM, but it is not known whether this effect persists in chronic pain states. In the present studies, persistent inflammation induced by complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) increased GABAergic miniature IPSCs (mIPSCs). Endocannabinoid activation of cannabinoid (CB1) receptors known to inhibit presynaptic GABA release was significantly reduced in the RVM of CFA-treated rats compared with naive rats. The reduction in CFA-treated rats correlated with decreased CB1 receptor protein expression and function in the RVM. Paradoxically, the nonselective CB1/CB2 receptor agonist WIN55212 inhibited GABAergic mIPSCs in both naive and CFA-treated rats. However, WIN55212 inhibition was reversed by the CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant in naive rats but not in CFA-treated rats. WIN55212-mediated inhibition in CFA-treated rats was blocked by the CB2 receptor-selective antagonist SR144528, indicating that CB2 receptor function in the RVM is increased during persistent inflammation. Consistent with these results, CB2 receptor agonists AM1241 and GW405833 inhibited GABAergic mIPSC frequency only in CFA-treated rats, and the inhibition was reversed with SR144528. When administered alone, SR144528 and another CB2 receptor-selective antagonist AM630 increased mIPSC frequency in the RVM of CFA-treated rats, indicating that CB2 receptors are tonically activated by endocannabinoids. Our data provide evidence that CB2 receptor function emerges in the RVM in persistent inflammation and that selective CB2 receptor agonists may be useful for treatment of persistent inflammatory pain.
Significance statement: These studies demonstrate that endocannabinoid signaling to CB1 and CB2 receptors in adult rostral ventromedial medulla is altered in persistent inflammation. The emergence of CB2 receptor function in the rostral ventromedial medulla provides additional rationale for the development of CB2 receptor-selective agonists as useful therapeutics for chronic inflammatory pain.
Keywords: GABAergic transmission; RVM; endocannabinoids; persistent inflammation; whole-cell patch clamp.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/370626-11$15.00/0.
Figures
References
-
- Ashton JC, Milligan ED. Cannabinoids for the treatment of neuropathic pain: clinical evidence. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;9:65–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
