A novel microRNA located in the TrkC gene regulates the Wnt signaling pathway and is differentially expressed in colorectal cancer specimens
- PMID: 28100780
- PMCID: PMC5418054
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.760710
A novel microRNA located in the TrkC gene regulates the Wnt signaling pathway and is differentially expressed in colorectal cancer specimens
Abstract
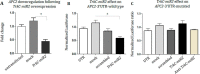
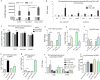
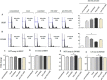
Tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC) is involved in cell survival, apoptosis, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. TrkC diverse functions might be attributed to the hypothetical non-coding RNAs embedded within the gene. Using bioinformatics approaches, a novel microRNA named TrkC-miR2 was predicted within the TrkC gene capable of regulating the Wnt pathway. For experimental verification of this microRNA, the predicted TrkC-premir2 sequence was overexpressed in SW480 cells, which led to the detection of two mature TrkC-miR2 isomiRs, and their endogenous forms were detected in human cell lines as well. Later, an independent promoter was deduced for TrkC-miR2 after the treatment of HCT116 cells with 5-azacytidine, which resulted in differential expression of TrkC-miR2 and TrkC host gene. RT-quantitative PCR and luciferase assays indicated that the APC2 gene is targeted by TrkC-miR2, and Wnt signaling is up-regulated. Also, Wnt inhibition by using small molecules along with TrkC-miR2 overexpression and TOP/FOP flash assays confirmed the positive effect of TrkC-miR2 on the Wnt pathway. Consistently, TrkC-miR2 overexpression promoted SW480 cell survival, which was detected by flow cytometry, MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assays, and crystal violate analysis. RT-qPCR analysis revealed that TrkC-miR2 is significantly up-regulated (∼70 times) in colorectal tumor tissues compared with their normal pairs. Moreover, the TrkC-miR2 expression level discriminated grades of tumor malignancies, which was consistent with its endogenous levels in HCT116, HT29, and SW480 colorectal cancer cell lines. Finally, an opposite expression pattern was observed for TrkC-miR2 and the APC2 gene in colorectal cancer specimens. In conclusion, here we introduce TrkC-miR2 as a novel regulator of Wnt signaling, which might be a candidate oncogenic colorectal cancer biomarker.
Keywords: Biomarker; Colorectal cancer; Survival; TrkC-miR2; Wnt signaling; annexin; biomarker; cancer; cell cycle; colorectal cancer.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- McGregor L. M., McCune B. K., Graff J. R., McDowell P. R., Romans K. E., Yancopoulos G. D., Ball D. W., Baylin S. B., and Nelkin B. D. (1999) Roles of trk family neurotrophin receptors in medullary thyroid carcinoma development and progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 4540–4545 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Genevois A.-L., Ichim G., Coissieux M.-M., Lambert M.-P., Lavial F., Goldschneider D., Jarrosson-Wuilleme L., Lepinasse F., Gouysse G., Herceg Z., Scoazec J. Y., Tauszig-Delamasure S., and Mehlen P. (2013) Dependence receptor TrkC is a putative colon cancer tumor suppressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 3017–3022 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jin W., Kim G. M., Kim M. S., Lim M. H., Yun C., Jeong J., Nam J.-S., and Kim S.-J. (2010) TrkC plays an essential role in breast tumor growth and metastasis. Carcinogenesis 31, 1939–1947 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

