Significant Association of Serum Adiponectin and Creatine Kinase-MB Levels in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 28100880
- PMCID: PMC5556187
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.38232
Significant Association of Serum Adiponectin and Creatine Kinase-MB Levels in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Aims: Adiponectin, an adipocyte-specific secretory protein, abundantly exists in the blood stream while its concentration paradoxically decreases in obesity. Hypoadiponectinemia is one of risks of cardiovascular diseases. However, impact of serum adiponectin concentration on acute ischemic myocardial damages has not been fully clarified. The present study investigated the association of serum adiponectin and creatine kinase (CK)-MB levels in subjects with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods: This study is a physician-initiated observational study and is also registered with the University Hospital Medical Information Network (Number: UMIN 000014418). Patients were admitted to Senri Critical Care Medical Center, given a diagnosis of STEMI, and treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Finally, 49 patients were enrolled and the association of serum adiponectin, CK-MB, and clinical features were mainly analyzed.
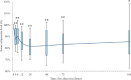
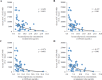
Results: Serum adiponectin levels decreased rapidly and reached the bottom at 24 hours after recanalization. Such reduction of serum adiponectin was inversely correlated with the area under the curve (AUC) of serum CK-MB (p=0.013). Serum adiponectin concentrations were inversely correlated with AUC of serum CK-MB. In multivariate analysis, serum adiponectin concentration on admission (p=0.002) and collateral (p=0.037) were significantly and independently correlated with serum AUC of CK-MB.
Conclusion: Serum AUC of CK-MB in STEMI subjects was significantly associated with serum adiponectin concentration on admission and reduction of serum adiponectin levels from baseline to bottom. The present study may provide a possibility that serum adiponectin levels at acute phase are useful in the prediction for prognosis after PCI-treated STEMI subjects.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Adiponectin; CK-MB; Infarct size; Myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflict of interests in present study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Time-Series Change of Serum Soluble T-Cadherin Concentrations and Its Association with Creatine Kinase-MB Levels in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022 Dec 1;29(12):1823-1834. doi: 10.5551/jat.63305. Epub 2022 Jul 20. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022. PMID: 35228485 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of Left Ventricular Mass and Infarct Size in Anterior Wall ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction (from the EMBRACE STEMI Clinical Trial).Am J Cardiol. 2016 Sep 1;118(5):625-31. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.06.025. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Am J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27392509 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic implications of creatine kinase-MB measurements in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Am Heart J. 2014 Oct;168(4):503-511.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Am Heart J. 2014. PMID: 25262260 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote Ischemic Postconditioning (RIPC) of the Upper Arm Results in Protection from Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Following Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) for Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI).Med Sci Monit. 2018 Feb 19;24:1017-1026. doi: 10.12659/msm.908247. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29456238 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic value of creatine kinase-myocardial band isoenzyme elevation following percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 May;81(6):959-67. doi: 10.1002/ccd.24542. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 22744792 Review.
Cited by
-
High Serum Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 5 Levels Associates with Early Improvement of Cardiac Function Following ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treated by Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Oct 1;26(10):868-878. doi: 10.5551/jat.47019. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30773518 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum adiponectin predicts improved coronary flow and clinical outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Jun;33(5):e22864. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22864. Epub 2019 Feb 19. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 30779470 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Time-Series Change of Serum Soluble T-Cadherin Concentrations and Its Association with Creatine Kinase-MB Levels in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022 Dec 1;29(12):1823-1834. doi: 10.5551/jat.63305. Epub 2022 Jul 20. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022. PMID: 35228485 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Dependent Change in Omentin-1 Level Correlated with Early Improvement of Myocardial Function in Patients with First Anterior ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction After Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Oct 1;26(10):856-867. doi: 10.5551/jat.47043. Epub 2019 Mar 9. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30853697 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Serum Adipolin with Epicardial Fat Thickness and Severity of Coronary Artery Diseases in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stable Angina Pectoris Patients.Med Princ Pract. 2021;30(1):52-61. doi: 10.1159/000508834. Epub 2020 May 21. Med Princ Pract. 2021. PMID: 32438366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I: Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2004; 24: 29-33 - PubMed
-
- Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y: Adiponectin and the cardiometabolic syndrome: an epidemiological perspective. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2014; 28: 93-106 - PubMed
-
- Maeda N, Funahashi T, Shimomura I: Cardiovascularmetabolic impact of adiponectin and aquaporin. Endocr J, 2013; 60: 251-259 - PubMed
-
- Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y: Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation, 1999; 100: 2473-2476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

