Successful Management in a Case of Traumatic Retinal Detachment due to Open Globe Injury Using Microincisional Vitrectomy
- PMID: 28101038
- PMCID: PMC5216252
- DOI: 10.1159/000450638
Successful Management in a Case of Traumatic Retinal Detachment due to Open Globe Injury Using Microincisional Vitrectomy
Abstract
Background: Retinal detachment (RD) following ocular trauma often results in guarded visual prognosis and sometimes leads to loss of the eye. With the advent of microincisional vitrectomy surgery and the development of surgical techniques, the management of ocular trauma has been transformed.
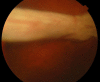
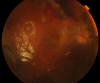
Case presentation: A 34-year-old man sustained an open globe injury from fragmented glass at work. He received primary repair and another follow-up surgery 9 days later, including vitrectomy, silicone oil tamponade, and lensectomy for RD and traumatic cataract at another medical center. However, his retina was totally detached and completely curled up in a roll with choroid on display when he was seen by us 1 month later. He was managed with vigilant and patient peeling and unfolding of the retina using a 23-gauge forceps and silicone oil tamponade, and achieved anatomical success and preservation of his eye at 6-month follow-up.
Conclusions: This report demonstrates that even in cases which appear to be hopeless at presentation, the surgeon's perseverance and surgical technique can salvage an eye that may otherwise be phthisical. It also encourages retinal surgeons to use microincisional vitrectomy to manage severe traumatic RD.
Keywords: Open globe injury; Traumatic retinal detachment; Vitrectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. The authors have no proprietary or commercial interest in any of the materials discussed in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgical Management of Traumatic Retinal Detachment with Primary Vitrectomy in Adult Patients.J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:5084319. doi: 10.1155/2017/5084319. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28163930 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Management of a Case of a 360-Degree Giant Retinal Break.Ophthalmologica. 2016;235(4):241. doi: 10.1159/000444811. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Ophthalmologica. 2016. PMID: 26959828
-
OUTCOMES OF VITRECTOMY WITH SILICONE OIL TAMPONADE FOR MANAGEMENT OF RETINAL DETACHMENT IN EYES WITH CHORIORETINAL COLOBOMA.Retina. 2019 Apr;39(4):736-742. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002014. Retina. 2019. PMID: 29280939
-
Pars plana lensectomy, pars plana vitrectomy, and silicone oil tamponade as initial management of cataract and combined traction/rhegmatogenous retinal detachment involving the macula associated with severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2003 Jul-Aug;34(4):270-8. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2003. PMID: 12875454
-
23-gauge vitrectomy assisted by combined endoscopy and a wide-angle viewing system for retinal detachment with severe penetrating corneal injury: a case report.Clin Ophthalmol. 2011;5:1767-70. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S25373. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 22267909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin H, Lema GM, Yoganathan P. Prognostic indicators of visual acuity after open globe injury and retinal detachment repair. Retina. 2016;36:750–757. - PubMed
-
- Chee YE, Patel MM, Vavvas DG. Retinal detachment after open-globe injury. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2013;53:79–92. - PubMed
-
- Coles WH, Haik GM. Vitrectomy in intraocular trauma. Its rationale and its indications and limitations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1972;87:621–628. - PubMed
-
- Vatne HO, Syrdalen P. Vitrectomy in double perforating eye injuries. Acta Ophthalmol. 1985;63:552–556. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous