New Candidate Genes Affecting Rice Grain Appearance and Milling Quality Detected by Genome-Wide and Gene-Based Association Analyses
- PMID: 28101096
- PMCID: PMC5209347
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01998
New Candidate Genes Affecting Rice Grain Appearance and Milling Quality Detected by Genome-Wide and Gene-Based Association Analyses
Abstract
Appearance and milling quality are two crucial properties of rice grains affecting its market acceptability. Understanding the genetic base of rice grain quality could considerably improve the high quality breeding. Here, we carried out an association analysis to identify QTL affecting nine rice grain appearance and milling quality traits using a diverse panel of 258 accessions selected from 3K Rice Genome Project and evaluated in two environments Sanya and Shenzhen. Genome-wide association analyses using 22,488 high quality SNPs identified 72 QTL affecting the nine traits. Combined gene-based association and haplotype analyses plus functional annotation allowed us to shortlist 19 candidate genes for seven important QTL regions affecting the grain quality traits, including two cloned genes (GS3 and TUD), two fine mapped QTL (qGRL7.1 and qPGWC7) and three newly identified QTL (qGL3.4, qGW1.1, and qGW10.2). The most likely candidate gene(s) for each important QTL were also discussed. This research demonstrated the superior power to shortlist candidate genes affecting complex phenotypes by the strategy of combined GWAS, gene-based association and haplotype analyses. The identified candidate genes provided valuable sources for future functional characterization and genetic improvement of rice appearance and milling quality.
Keywords: GWAS; chalkiness; gene-based association analysis; grain shape; milling; rice.
Figures
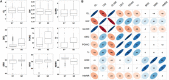
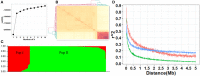
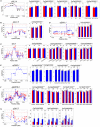
References
-
- Bai X., Luo L., Yan W., Kovi M. R., Zhan W., Xing Y. (2010). Genetic dissection of rice grain shape using a recombinant inbred line population derived from two contrasting parents and fine mapping a pleiotropic quantitative trait locus qGL7. BMC Genet. 11:16. 10.1186/1471-2156-11-16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen H. M., Zhao Z. G., Jiang L., Wan X. Y., Liu L. L., Wu X. J., et al. (2011). Molecular genetic analysis on percentage of grains with chalkiness in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10, 6891–6903. 10.5897/AJB11.208 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

