Endothelium-dependent vasodilation effects of Panax notoginseng and its main components are mediated by nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase pathways
- PMID: 28101178
- PMCID: PMC5228079
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3890
Endothelium-dependent vasodilation effects of Panax notoginseng and its main components are mediated by nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase pathways
Abstract
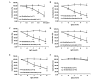
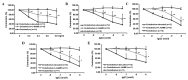
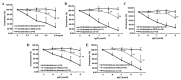
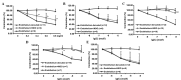
Panax notoginseng, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, has been used for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. The main bioactive components of this species are Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS). The present study aimed to investigate the effects of PNS and five of its main components (ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rb1 and Rd, and notoginsenoside R1) on rat aorta rings pre-contracted with norepinephrine (NE) and to determine the underlying mechanism of action. Isolated aorta rings (with or without intact endothelium) from adult male Wistar rats were stimulated with NE to induce vasoconstriction, and subsequently treated with different concentrations of PNS and its five main components (Rg1, Re, Rb1, R1 and Rd) separately. This procedure was repeated after pre-incubation with the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), the guanylate cyclase inhibitor 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) and the cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor indomethacin (INDO), in order to elucidate the mechanism of action of PNS and its components. The results demonstrated that PNS and the components Rg1, Re, Rb1 and R1, but not Rd, induced vessel relaxation in a concentration-dependent manner when the endothelium lining was intact. NO synthase inhibitor L-NAME and guanylate cyclase inhibitor ODQ attenuated the diastolic effects of PNS, Rg1, Re, Rb1 and R1 in aortic rings with intact endothelium. By contrast, INDO, a known COX inhibitor weakened the vasodilation effects of PNS, Re and Rb1 but demonstrated no effect on Rg1 and R1. In conclusion, PNS and two of its main components (Re and Rb1) exert vasodilating effects through the NO and COX pathways.
Keywords: Panax notoginseng saponins; aortic ring; cyclooxygenase; ginsenoside Rb1; ginsenoside Rd; ginsenoside Re; ginsenoside Rg1; nitric oxide; notoginsenoside R1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of the Combination of the Main Active Components of Astragalus and Panax notoginseng on Inflammation and Apoptosis of Nerve Cell after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7):1419-38. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500809. Epub 2015 Oct 18. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26477799
-
Inhibiting adhesion events by Panax notoginseng saponins and Ginsenoside Rb1 protecting arteries via activation of Nrf2 and suppression of p38 - VCAM-1 signal pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:423-430. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27620662
-
Simultaneous determination of three major bioactive saponins of Panax notoginseng using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and a pharmacokinetic study.Chin Med. 2010 Mar 23;5:12. doi: 10.1186/1749-8546-5-12. Chin Med. 2010. PMID: 20331853 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of panax notoginseng saponins on cardiovascular diseases: a comprehensive overview of experimental studies.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:204840. doi: 10.1155/2014/204840. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25152758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-layered effects of Panax notoginseng on immune system.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Jun;204:107203. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107203. Epub 2024 May 6. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38719196 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional chinese medicine in coronary microvascular disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:929159. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.929159. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focus on Notoginsenoside R1 in Metabolism and Prevention Against Human Diseases.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Feb 7;14:551-565. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S240511. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32103897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panax Notoginseng Saponins: A Review of Its Mechanisms of Antidepressant or Anxiolytic Effects and Network Analysis on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Molecules. 2018 Apr 17;23(4):940. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040940. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29673237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Endothelium-Dependent and -Independent Vasodilation Induced by Phytochemicals in Isolated Rat Aorta.Animals (Basel). 2019 Aug 29;9(9):623. doi: 10.3390/ani9090623. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31470540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The integration of spear and shield: a panoramic analysis of the blood circulation-promoting and hemostatic effects of Panax notoginseng.Chin Med. 2025 May 29;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01100-6. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40442777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Jr, Roccella EJ. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2010;289:2560–2572. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.19.2560. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
