Acute renal injury induced by valacyclovir hydrochloride: A case report
- PMID: 28101180
- PMCID: PMC5228316
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3905
Acute renal injury induced by valacyclovir hydrochloride: A case report
Abstract
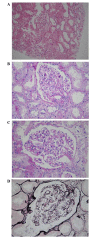
Acyclovir has been a frequently used antiviral agent in the clinical treatment of leukemia, acute encephalitis, malignant tumor and herpes simplex. The adverse effects of this drug have been widely described in clinical practice. In the present study, a case of a 35-year-old female patient diagnosed with herpes simplex, who developed acute renal injury following treatment with valacyclovir hydrochloride, is described. Kidney biopsy, light microscopy and laboratory examination were performed, and all findings revealed the signs of evident vacuolar degeneration of capillary endothelial and renal tubular epithelial cells, erythrocyte aggregation in partial renal tubule and microvilli exfoliation from epithelial cells. Renal interstitial edema was clearly identified. The clinical evidence observed from this female patient indicated that renal functions should be closely monitored during valacyclovir hydrochloride administration. A variety of effective measures, such as hydration, alkalizing urine, promoting the discharge of medication and the use of antagonists are recommended following the administration of antiviral agents.
Keywords: acute renal injury; acyclovir; adverse event; herpes simples.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Valacyclovir-induced Neurotoxicity in a Patient with a Preserved Renal Function.Intern Med. 2018 Nov 1;57(21):3213-3216. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0403-17. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29877263 Free PMC article.
-
Acute renal failure with acyclovir treatment in a child with leukemia.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2010 Apr;33(2):217-9. doi: 10.3109/01480540903311076. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20307148
-
Oral valacyclovir as prophylaxis against herpes simplex virus reactivation during high dose chemotherapy for leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2004 Nov;45(11):2215-9. doi: 10.1080/10428190410001733763. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. PMID: 15512809 Clinical Trial.
-
[Acyclovir-induced neurotoxicity and acute kidney injury in an elderly diabetic patient treated with valacyclovir: report of a case].Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2014;51(6):581-5. doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.51.581. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25749332 Review. Japanese.
-
Valacyclovir for the treatment of genital herpes.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2006 Jun;4(3):367-76. doi: 10.1586/14787210.4.3.367. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2006. PMID: 16771614 Review.
Cited by
-
HMBA ameliorates obesity by MYH9- and ACTG1-dependent regulation of hypothalamic neuropeptides.EMBO Mol Med. 2023 Dec 7;15(12):e18024. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202318024. Epub 2023 Nov 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37984341 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Evaluation for Acute Kidney Injury Induced by the Concomitant Use of Valacyclovir, Analgesics, and Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors: The Detection of Signals of Drug-Drug Interactions.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 8;10:874. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00874. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31440161 Free PMC article.
-
Valacyclovir-induced neurotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in an elderly patient with a history of nephrectomy: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2025 May 30;26(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-03941-7. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40447999 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomal siRNA Formulations for the Treatment of Herpes Simplex Virus-1: In Vitro Characterization of Physicochemical Properties and Activity, and In Vivo Biodistribution and Toxicity Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 13;14(3):633. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030633. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35336008 Free PMC article.
-
Valacyclovir-associated acute kidney injury.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Jun 28;15(6):e249552. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2022-249552. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35764333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tomori K, Isozumi K, Motohashi S, Komatsumoto S, Fukuuchi Y. A young patient of acute encephalitis complicated with acyclovir encephalopathy without renal dysfunction. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2003;43:470–476. (In Japanese) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
