Bevacizumab, pemetrexed and carboplatin in first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer patients: Focus on patients with brain metastases
- PMID: 28101218
- PMCID: PMC5228302
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5268
Bevacizumab, pemetrexed and carboplatin in first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer patients: Focus on patients with brain metastases
Abstract
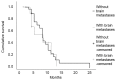
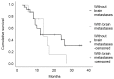
Data concerning bevacizumab plus pemetrexed plus carboplatin as first-line treatment for patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with or without brain metastases (BM) are lacking. The present study analyzed the efficacy and safety of this combination as induction therapy, followed by maintenance therapy with bevacizumab plus pemetrexed in non-squamous NSCLC patients with or without BM. Treatment-naïve patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status score of 0-2 were eligible. Treatment consisted of carboplatin (area under the curve of 5), pemetrexed (500 mg/m2) and bevacizumab (15 mg/kg) every 3 weeks for 6 cycles. Responders and patients with stable disease received maintenance therapy with bevacizumab plus pemetrexed until disease progression, which was evaluated every 3 cycles, or unacceptable toxicity. Kaplan-Meier median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) times were the primary endpoints, and safety was the secondary endpoint. In total, 39 patients, aged 44-78 years (median, 60 years), were treated; 11 (28.2%) of whom presented with BM. The majority of patients (56.4%) completed 6 cycles of induction therapy, and 26 patients continued on to maintenance therapy. The median PFS time was 8.2 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 7.05-9.35] and the median OS time was 14.0 months (95% CI, 8.46-19.54). Median PFS and OS times did not differ significantly between patients with or without BM (log rank (Mantel-Cox): PFS, P=0.748 and OS, P=0.447). The majority of patients (76.9%) did not experience adverse events during treatment. Overall, bevacizumab plus pemetrexed plus carboplatin as induction therapy, followed by bevacizumab plus pemetrexed as maintenance therapy was effective and well tolerated in advanced NSCLC, whether brain metastases were present or not.
Keywords: bevacizumab; brain metastases; carboplatin; carcinoma; chemotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; pemetrexed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase II study of carboplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab followed by erlotinib and bevacizumab maintenance for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer with wild-type EGFR (HOT1101).Int J Clin Oncol. 2018 Dec;23(6):1060-1069. doi: 10.1007/s10147-018-1318-z. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30027464 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II Trial of Carboplatin and Pemetrexed Plus Bevacizumab with Maintenance Bevacizumab as a First-line Treatment for Advanced Non-squamous Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Elderly Patients.Anticancer Res. 2018 Jun;38(6):3779-3784. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12661. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29848743 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized Phase III Study of Continuation Maintenance Bevacizumab With or Without Pemetrexed in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: COMPASS (WJOG5610L).J Clin Oncol. 2020 Mar 10;38(8):793-803. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01494. Epub 2019 Dec 27. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31880966 Clinical Trial.
-
Maintenance treatment of combination with bevacizumab vs single agent for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 6;100(31):e26862. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026862. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34397863 Free PMC article.
-
Pemetrexed in maintenance treatment of advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2015 Jan 29;6:13-25. doi: 10.2147/LCTT.S73268. eCollection 2015. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2015. PMID: 28210147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy in symptomatic brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Nov;11(11):4725-4734. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.10.49. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31903262 Free PMC article.
-
PET-CT evaluation of the curative effect of crizotinib on malignant myofibroblastoma with rare mutation of ALK R401: a case report and literature review.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Apr 5;11:1921-1927. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S155033. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29670367 Free PMC article.
-
Newly developed anti-angiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 26;9(11):10147-10163. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23755. eCollection 2018 Feb 9. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29515799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First-line pemetrexed and carboplatin plus anlotinib for epidermal growth factor receptor wild-type and anaplastic lymphoma kinase-negative lung adenocarcinoma with brain metastasis: A case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 4;99(36):e22128. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022128. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32899099 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-22 enhanced the efficacy of icotinib plus pemetrexed in a rat model of non-small cell lung cancer.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Mar;23(3):329-336. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2019.39291.9320. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32440319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atlas of cancer mortality in the European union and the European Economic Area: 1993–1997. IARC Sci Publ. 2008:1–259. - PubMed
-
- Besse B, Adjei A, Baas P, Meldgaard P, Nicolson M, Paz-Ares L, Reck M, Smit EF, Syrigos K, Stahel R, et al. 2nd ESMO consensus conference on lung cancer: Non-small-cell lung cancer first-line/second and further lines of treatment in advanced disease. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1475–1484. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu123. - DOI - PubMed
-
- NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, corp-author. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version I. 2015
-
- National Cancer Institute, corp-author. PDQ® Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; Accessed Nov 26, 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources