Detection of microRNA-200b may predict the inhibitory effect of gefitinib on non-small cell lung cancer and its potential mechanism
- PMID: 28101246
- PMCID: PMC5228080
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.5365
Detection of microRNA-200b may predict the inhibitory effect of gefitinib on non-small cell lung cancer and its potential mechanism
Abstract
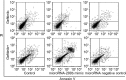
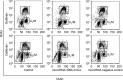
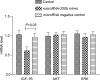
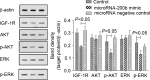
The present study aimed to investigate the association and underlying mechanisms between microRNA-200b level and the inhibitory effect of gefitinib on non-small cell lung cancer. In total, 100 patients (43 males and 57 females; median age, 63 years) with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were selected. All patients were administered with gefitinib orally (250 mg/day) and the effect of gefitinib was evaluated according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors guidelines. Tumor tissue and plasma samples were collected prior to and subsequent to therapy. The microRNA-200b levels in tissues and plasma were determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A549 cells were cultured in vitro and transfected with microRNA-200b mimic. Using Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, the proliferation inhibition detected was induced by 0.1 µM gefitinib in transfected or non-transfected A549 cells. Cell apoptosis and cell cycle progression were analyzed by flow cytometry and the migration of cells was observed by Transwell assay. In addition, mRNA and protein levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R), protein kinase B (AKT) and extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK), together with the phosphorylation of AKT and ERK in A549 cells, were determined by quantitative PCR and western blot analysis, respectively. The microRNA-200b levels in gefitinib-insensitive patients were decreased compared with gefitinib-sensitive patients. Transfection with microRNA-200b mimic increased the gefitinib induced proliferation inhibition, apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in A549 cells. Also, transfection with microRNA-200b mimic increased the migration inhibitory effect of gefitinib on A549 cells. Decreased IGF-1R expression together with reduced phosphorylation of AKT and ERK were observed following transfection of A549 cells with the microRNA 200b mimic. In conclusion, detection of microRNA-200b may predict the inhibitory effect of gefitinib on NSCLC. Upregulation of microRNA-200b led to the elevated sensitivity of glioma cells to gefitinib, and this effect may be explained as microRNA-200b being able to inhibit the expression of IGF-1R, thereby reducing the activation of downstream phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
Keywords: IGF-1R; gefitinib; microRNA; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-497 may enhance the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to gefitinib through targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Oct;10(10):5889-5897. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.40. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30505497 Free PMC article.
-
The long non-coding RNA, GAS5, enhances gefitinib-induced cell death in innate EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells with wide-type EGFR via downregulation of the IGF-1R expression.J Hematol Oncol. 2015 Apr 29;8:43. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0140-6. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25925741 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNAs involved in gefitinib resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer through the insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Oct;14(4):2853-2862. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4847. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28912847 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1431-1446. doi: 10.1159/000479207. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715819
-
The relationship between miR-17-5p, miR-92a, and let-7b expression with non-small cell lung cancer targeted drug resistance.J BUON. 2017 Mar-Apr;22(2):454-461. J BUON. 2017. PMID: 28534369
Cited by
-
MLH1 enhances the sensitivity of human endometrial carcinoma cells to cisplatin by activating the MLH1/c-Abl apoptosis signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2018 Dec 29;18(1):1294. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5218-4. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30594176 Free PMC article.
-
miR-497 may enhance the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells to gefitinib through targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Oct;10(10):5889-5897. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.10.40. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30505497 Free PMC article.
-
Methyloleanolate Induces Apoptotic And Autophagic Cell Death Via Reactive Oxygen Species Generation And c-Jun N-terminal Kinase Phosphorylation.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Oct 23;12:8621-8635. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S211904. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31695422 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-142-3p increases radiosensitivity in human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells by inhibiting the expression of CD133.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 4;8(1):5674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23968-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29618746 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200b is a potential biomarker of the expression of PD-L1 in patients with lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Oct;11(10):2975-2982. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13653. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32893980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roemans P, Emami B, Cox J, Pacagnella A, Holsti L, Monteau M, Helle P, Comis R, Schaake C. Quality control in NSCLC treatment: A consensus report. Lung Cancer. 1991;7:19–20. doi: 10.1016/0169-5002(91)90007-S. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
