Endoscopic sensing of alveolar pH
- PMID: 28101415
- PMCID: PMC5231296
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.8.000243
Endoscopic sensing of alveolar pH
Abstract
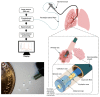
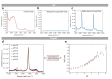
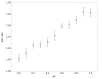
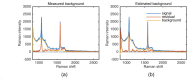
Previously unobtainable measurements of alveolar pH were obtained using an endoscope-deployable optrode. The pH sensing was achieved using functionalized gold nanoshell sensors and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The optrode consisted of an asymmetric dual-core optical fiber designed for spatially separating the optical pump delivery and signal collection, in order to circumvent the unwanted Raman signal generated within the fiber. Using this approach, we demonstrate a ~100-fold increase in SERS signal-to-fiber background ratio, and demonstrate multiple site pH sensing with a measurement accuracy of ± 0.07 pH units in the respiratory acini of an ex vivo ovine lung model. We also demonstrate that alveolar pH changes in response to ventilation.
Keywords: (170.4580) Optical diagnostics for medicine; (170.6510) Spectroscopy, tissue diagnostics.
Figures


References
-
- Pezzulo A. A., Tang X. X., Hoegger M. J., Abou Alaiwa M. H., Ramachandran S., Moninger T. O., Karp P. H., Wohlford-Lenane C. L., Haagsman H. P., van Eijk M., Bánfi B., Horswill A. R., Stoltz D. A., McCray P. B., Jr, Welsh M. J., Zabner J., “Reduced airway surface pH impairs bacterial killing in the porcine cystic fibrosis lung,” Nature 487(7405), 109–113 (2012). 10.1038/nature11130 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jayaraman S., Song Y., Verkman A. S., “Airway surface liquid pH in well-differentiated airway epithelial cell cultures and mouse trachea,” Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 281(5), C1504–C1511 (2001). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
