Overview of Albumin and Its Purification Methods
- PMID: 28101456
- PMCID: PMC5241407
- DOI: 10.15171/apb.2016.063
Overview of Albumin and Its Purification Methods
Abstract
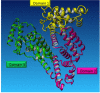
As the most frequent plasma protein, albumin constitutes more than 50% of the serum proteins in healthy individuals. It has a key role in oncotic pressure maintenance and it is known as a versatile protein carrier for transportation of various endogenous and exogenous ligands. Reduced amounts of albumin in the body will lead to different kinds of diseases such as hypovolemia and hypoproteinemia. It also has various indications in shocks, burns, cardiopulmonary bypass, acute liver failure and etc. Further applications in research consist of cell culture supplement, drug delivery carrier and protein/drug stabilizer. So, the demand for albumin increased annually worldwide. Due to different applications of albumin, many efforts have been accomplished to achieve albumin during a long period of time. In this review, an overview of serum albumin and different purification methods are summarized.
Keywords: Chromatography; Human serum albumin; Immunoaffinity; Purification.
References
-
- Hirose M, Tachibana A, Tanabe T. Recombinant human serum albumin hydrogel as a novel drug delivery vehicle. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30(5):664–9. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2010.02.020. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials