Inhibitory effect of saliva on osteoclastogenesis in vitro requires toll-like receptor 4 signaling
- PMID: 28101679
- PMCID: PMC5632348
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-016-2041-7
Inhibitory effect of saliva on osteoclastogenesis in vitro requires toll-like receptor 4 signaling
Abstract
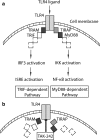
Objectives: Saliva can suppress osteoclastogenesis, but the underlying mechanism has not been discovered yet. Considering that endotoxins suppress osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow cultures and that saliva contains endotoxins, it was reasonable to hypothesize that the impact of saliva on osteoclastogenesis requires toll-like receptor 4 signaling.
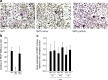
Material and methods: To test this hypothesis, we blocked toll-like receptor 4 signaling with TAK-242 in the presence of saliva in murine bone marrow cultures. Osteoclastogenesis was evaluated based on gene expression analysis and histochemical staining for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. Resorption was performed on dentine.
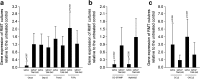
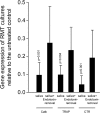
Results: We report that TAK-242 reversed the inhibitory effect of fresh sterile saliva on the formation of multinucleated cells that stained positive for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. In line with this finding, TAK-242 increased the expression of the osteoclast functional genes cathepsin K, calcitonin receptor, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in the presence of saliva. TAK-242 also supported the expression of NFATc1, the master regulator of osteoclastogenesis, as well as DC-STAMP and Atp6v0d2, both being cell fusion genes. In support of the hypothesis, depletion of saliva from endotoxin partially reversed the inhibitory effect on osteoclastogenesis. Moreover, salivary pellicle on plastic and titanium did not affect osteoclastogenesis.
Conclusion: Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling revealed that saliva can contribute to innate immunity by preventing hematopoietic progenitors to become osteoclasts.
Clinical relevance: Saliva can activate pattern recognition receptor signaling through endotoxins and other stress factors, indicating the demand for macrophages rather than for osteoclasts.
Keywords: Dentistry; Endotoxin; Murine bone marrow; Osteoclast; Saliva; Toll-like receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the ethical board of the Canton of Bern (No. BE76/12).
Funding
The work was supported and conducted at the Department of Preventive, Restorative and Pediatric Dentistry, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern, Switzerland.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Saliva suppresses osteoclastogenesis in murine bone marrow cultures.J Dent Res. 2015 Jan;94(1):192-200. doi: 10.1177/0022034514553977. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25297116
-
Calcium-containing crystals enhance receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-mediated osteoclastogenesis via extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and p38 pathways.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Oct;54(10):1913-22. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev107. Epub 2015 May 20. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25998451
-
Conditioned medium from fresh and demineralized bone enhances osteoclastogenesis in murine bone marrow cultures.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016 Feb;27(2):226-32. doi: 10.1111/clr.12573. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016. PMID: 25754222
-
β-Adrenergic signaling stimulates osteoclastogenesis via reactive oxygen species.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Mar 1;304(5):E507-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00191.2012. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23169789
-
Feedback inhibition of osteoclastogenesis during inflammation by IL-10, M-CSF receptor shedding, and induction of IRF8.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Nov;1237:88-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06217.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 22082370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oral cell lysates reduce osteoclastogenesis in murine bone marrow cultures.Cytotechnology. 2025 Feb;77(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00688-1. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39781111 Free PMC article.
-
Saliva enhances infection of gingival fibroblasts by herpes simplex virus 1.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 3;14(10):e0223299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223299. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31581238 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin Upregulates microRNA-186 and Inhibits the TLR4-Mediated MAPKs/NF-κB Pathway to Relieve Steroid-Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 16;12:583975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.583975. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995003 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid PRF Reduces the Inflammatory Response and Osteoclastogenesis in Murine Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 9;12:636427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636427. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dawes C, Pedersen AM, Villa A, Ekstrom J, Proctor GB, Vissink A, Aframian D, McGowan R, Aliko A, Narayana N, Sia YW, Joshi RK, Jensen SB, Kerr AR, Wolff A. The functions of human saliva: a review sponsored by the world workshop on oral medicine VI. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60:863. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

