Inpatient Hospitalization Costs Associated with Birth Defects Among Persons of All Ages - United States, 2013
- PMID: 28103210
- PMCID: PMC5657658
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6602a1
Inpatient Hospitalization Costs Associated with Birth Defects Among Persons of All Ages - United States, 2013
Abstract
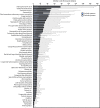
In the United States, major structural or genetic birth defects affect approximately 3% of live births (1) and are responsible for 20% of infant deaths (2). Birth defects can affect persons across their lifespan and are the cause of significant lifelong disabilities. CDC used the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) 2013 National Inpatient Sample (NIS), a 20% stratified sample of discharges from nonfederal community hospitals, to estimate the annual cost of birth defect-associated hospitalizations in the United States, both for persons of all ages and by age group. Birth defect-associated hospitalizations had disproportionately high costs, accounting for 3.0% of all hospitalizations and 5.2% of total hospital costs. The estimated annual cost of birth defect-associated hospitalizations in the United States in 2013 was $22.9 billion. Estimates of the cost of birth defect-associated hospitalizations offer important information about the impact of birth defects among persons of all ages on the overall health care system and can be used to prioritize prevention, early detection, and care.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. Update on overall prevalence of major birth defects—Atlanta, Georgia, 1978–2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2008;57:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Arias E. Mortality in the United States, 2012. NCHS Data Brief 2014;168:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Introduction to the HCUP National Inpatient Sample (NIS) 2013. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2015. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/nation/nis/NISIntroduction2013.pdf
-
- National Birth Defects Prevention Network. Appendix 3.1. Birth defects descriptions for NBDPN core, recommended, and extended conditions. In: Botto L, Carey J, Cassel C, et al., eds. Guidelines for conducting birth defects surveillance. Atlanta, GA: National Birth Defects Prevention Network; 2015.
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Cost-to-charge ratio files: 2013 National Inpatient Sample (NIS) user guide. Rockville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2015. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/state/CCR2013NISUserGuide.pdf
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

