A Superoxide Dismutase Capable of Functioning with Iron or Manganese Promotes the Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to Calprotectin and Nutritional Immunity
- PMID: 28103306
- PMCID: PMC5245786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006125
A Superoxide Dismutase Capable of Functioning with Iron or Manganese Promotes the Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to Calprotectin and Nutritional Immunity
Abstract
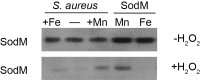
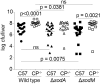
Staphylococcus aureus is a devastating mammalian pathogen for which the development of new therapeutic approaches is urgently needed due to the prevalence of antibiotic resistance. During infection pathogens must overcome the dual threats of host-imposed manganese starvation, termed nutritional immunity, and the oxidative burst of immune cells. These defenses function synergistically, as host-imposed manganese starvation reduces activity of the manganese-dependent enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD). S. aureus expresses two SODs, denoted SodA and SodM. While all staphylococci possess SodA, SodM is unique to S. aureus, but the advantage that S. aureus gains by expressing two apparently manganese-dependent SODs is unknown. Surprisingly, loss of both SODs renders S. aureus more sensitive to host-imposed manganese starvation, suggesting a role for these proteins in overcoming nutritional immunity. In this study, we have elucidated the respective contributions of SodA and SodM to resisting oxidative stress and nutritional immunity. These analyses revealed that SodA is important for resisting oxidative stress and for disease development when manganese is abundant, while SodM is important under manganese-deplete conditions. In vitro analysis demonstrated that SodA is strictly manganese-dependent whereas SodM is in fact cambialistic, possessing equal enzymatic activity when loaded with manganese or iron. Cumulatively, these studies provide a mechanistic rationale for the acquisition of a second superoxide dismutase by S. aureus and demonstrate an important contribution of cambialistic SODs to bacterial pathogenesis. Furthermore, they also suggest a new mechanism for resisting manganese starvation, namely populating manganese-utilizing enzymes with iron.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2013.
-
- Organization WH. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. 2014.
-
- Said-Salim B, Mathema B, Kreiswirth BN. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an emerging pathogen. Infection control and hospital epidemiology: the official journal of the Society of Hospital Epidemiologists of America. 2003;24(6):451–5. Epub 2003/06/28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

